Hugo 源码阅读
这篇源码阅读编写于 2020 年 12 月,原本出于自己想实现一个 Go 语言的静态博客生成器,开始阅读 Hugo 的源码,了解一些实现的细节与需要注意的地方,途中发现代码量巨大,而且内部实现逻辑较为复杂,在这里也只对部分逻辑进行了梳理(只是冰山一角)。
1. 概述
我阅读并作出中文注释的 Commits 可以在这里看到: https://github.com/mayocream/hugo/commits?author=mayocream
阅读源码的过程中也当 typofix 机器人提了 PR,毕竟自己确实没有能贡献的地方。不过阅读源码并注释帮助理解,方便整理也是一个好习惯,在工作中我逐渐学会了。
根据 Wikipedia 的记载,Hugo 早在 2013 年就发布了,直到去年我一直没有使用过,可能是它没有官方的中文文档,Go 语言对当时我也太生疏,而且 Hugo 的模板语法和 Hexo 与 Jekyll 也不一样,而且官方推荐用 Theme 的方式是 Git Submodule,相比于 Hexo 上手难度还是高一些。
现在作为使用者来说,Hugo 使用的 Go 模板语法很好用,Hugo 基于模板的 Pipeline 实现的数据预处理也非常方便,用了就停不下来了。而且基于 esbuild 的打包使得静态资源的构建也很方便,终于脱离 Webpack 了。我还有一个弃坑的项目 material-design-blog 也是使用的 Snowpack (esbuild) 进行静态资源的打包,不知道都已经是 2021 年末了,为什么公司的那群人还要使用 Webpack 缓慢地构建呢。
Hugo 现在基本上 Github 上开源项目文档发布的标配,不过 Cloudflare 的开发者文档是使用 Gatsby 发布的,可能 Cloudflare 内部 JavaScript 用得也多吧,Worker 对于 Go 就没有原生支持。
在使用过程中我还是尽量克制自己使用 Hugo Shortcodes,一个 Markdown 文档应该保持纯净,除了 Markdown 扩展语法以外都不要使用,需要特殊实现的也使用原生 HTML 标签,这样方便将写作和 Blog 发布分离。
我自己用在 Translations 项目中的 Hugo 的 Shortcode 是:
<figure class="manga">
<img src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/mayocream/Translations@gh-pages/raw/{{ .Get "src" }}" alt="" loading="lazy">
<figcaption>{{ .Get "alt" }}</figcaption>
</figure>
为了利用上 Figure 标签与 jsDelivr 的 CDN,使用了 Shortcode,不过该项目中采用 Hugo 是专门为了进行发布管理的,关于这个如果我还有时间做更多翻译的话,可能会写一篇文章来介绍翻译小工程的工作流 🤹。
1.1. 目录结构
Hugo 的开发时间较早,所以目录结构较为分散,与 Standard Go Project Layout 差异较大,当然这个社区提出的目录规范建议,也存在着争议,不过 Google 的不少项目都是遵循这个规范的,例如 Kubernetes 和 grpc-go。
$ tree -L 1 -d
.
├── commands // CLI 入口, 解析 flags
├── common // 工具类
├── hugofs // FS 封装, 基于 afero/fs
├── hugolib // 程序主逻辑
├── lazy // 懒加载工具包
├── livereload // Live 预览, 基于 Service Worker
├── markup // Markdown 解析相关
├── parser // 解析文件头
...
40 directories
2. 程序流程
2.1. 流程定义
2.1.1. 错误状态码
func main() {
resp := commands.Execute(os.Args[1:])
if resp.Err != nil {
if resp.IsUserError() {
resp.Cmd.Println("")
resp.Cmd.Println(resp.Cmd.UsageString())
}
os.Exit(-1)
}
}
os.Exit(-1) 程序的退出状态码不在 0~255 之间,会自动做转换,转换的规则如下1:
- 当指定的退出时状态码为负数:
256 - (|code| % 256)
- 当指定的退出时状态码为正数:
code % 256
由此程序退出的状态码为 255。
2.1.2. CLI 命令
// commands/commands.go
func (b *commandsBuilder) addAll() *commandsBuilder {
b.addCommands(
b.newServerCmd(),
newVersionCmd(),
newEnvCmd(),
b.newConfigCmd(),
newCheckCmd(),
b.newDeployCmd(),
b.newConvertCmd(),
b.newNewCmd(),
b.newListCmd(),
newImportCmd(),
newGenCmd(),
createReleaser(),
b.newModCmd(),
)
return b
}
所有的 cmd handler 继承自 basecmd,实现了 cmder 接口:
// commands/helpers.go
type cmder interface {
flagsToConfig(cfg config.Provider)
getCommand() *cobra.Command
}
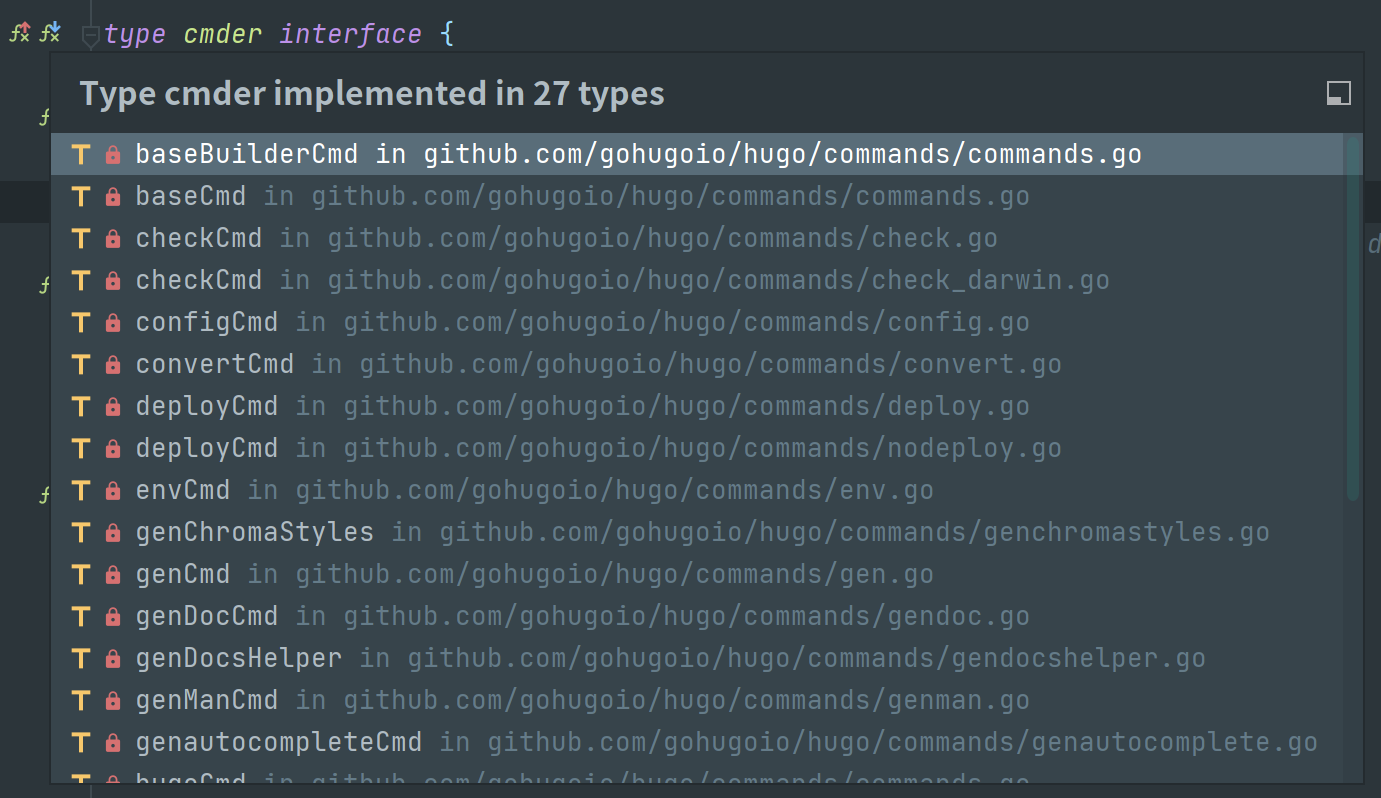
// commands/commands.go
func (b *commandsBuilder) addAll() *commandsBuilder {
b.addCommands(
b.newServerCmd(),
newVersionCmd(),
newEnvCmd(),
b.newConfigCmd(),
newCheckCmd(),
b.newDeployCmd(),
b.newConvertCmd(),
b.newNewCmd(),
b.newListCmd(),
newImportCmd(),
newGenCmd(),
createReleaser(),
b.newModCmd(),
)
return b
}
func (b *commandsBuilder) build() *hugoCmd {
// 添加主 hugo 命令
h := b.newHugoCmd()
// 将命令数组添加进 cobra 的 Root Command 中, 作为子命令
addCommands(h.getCommand(), b.commands...)
return h
}
2.2. 渲染初始化
执行 Hugo 命令时进行的初始化加载
// 创建 hugoCmd 封装块
func (b *commandsBuilder) newHugoCmd() *hugoCmd {
cc := &hugoCmd{}
cc.baseBuilderCmd = b.newBuilderCmd(&cobra.Command{
Use: "hugo",
Short: "hugo builds your site",
Long: `hugo is the main command, used to build your Hugo site.
Hugo is a Fast and Flexible Static Site Generator
built with love by spf13 and friends in Go.
Complete documentation is available at http://gohugo.io/.`,
// 执行渲染操作
RunE: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) error {
// 记录全局操作耗时
defer cc.timeTrack(time.Now(), "Total")
cfgInit := func(c *commandeer) error {
if cc.buildWatch {
// 如果开启了 watch 模式则关闭动态重载
c.Set("disableLiveReload", true)
}
return nil
}
// 初始化配置
c, err := initializeConfig(true, cc.buildWatch, &cc.hugoBuilderCommon, cc, cfgInit)
if err != nil {
return err
}
cc.c = c
// 编译操作
return c.build()
},
})
...
2.2.1. 配置文件加载
// hugolib/config.go
for _, configDir := range configDirs {
err := afero.Walk(sourceFs, configDir, func(path string, fi os.FileInfo, err error) error {
if fi == nil || err != nil {
return nil
}
if fi.IsDir() {
dirnames = append(dirnames, path)
return nil
}
// 检查文件后缀是否是支持的格式
if !config.IsValidConfigFilename(path) {
return nil
}
// 文件名, 移除文件后缀
name := helpers.Filename(filepath.Base(path))
// 加载文件内容到 map
item, err := metadecoders.Default.UnmarshalFileToMap(sourceFs, path)
if err != nil {
return l.wrapFileError(err, path)
}
var keyPath []string
// 如果不是 hugo 的 config 文件
if name != "config" {
// Can be params.jp, menus.en etc.
// 如果文件还有后缀, 可能是语言后缀
name, lang := helpers.FileAndExtNoDelimiter(name)
keyPath = []string{name}
// 如果语言后缀存在
if lang != "" {
// 填充语言文件夹路径
keyPath = []string{"languages", lang}
switch name {
case "menu", "menus":
keyPath = append(keyPath, "menus")
case "params":
keyPath = append(keyPath, "params")
}
}
}
root := item
if len(keyPath) > 0 {
root = make(map[string]interface{})
m := root
// 遍历形成层级关系
// 遍历语言文件夹的路径
// i 从 0 开始
for i, key := range keyPath {
// 如果 i >= 最后一个元素的 index
if i >= len(keyPath)-1 {
// 将文件内容填充到 key 下面
m[key] = item
} else {
nm := make(map[string]interface{})
m[key] = nm
m = nm
}
}
}
// Migrate menu => menus etc.
config.RenameKeys(root)
// 合并配置文件
if err := v.MergeConfigMap(root); err != nil {
return l.wrapFileError(err, path)
}
return nil
})
遍历配置文件夹、以及加载配置文件(yaml/toml/json 后缀)到 Map 中,使用 Viper 的 MergeConfigMap 载入配置,包含语言、菜单配置。
// hugolib/hugo_sites.go
// 创建 sites 的配置
func createSitesFromConfig(cfg deps.DepsCfg) ([]*Site, error) {
var sites []*Site
// 获取多语言配置
languages := getLanguages(cfg.Cfg)
for _, lang := range languages {
if lang.Disabled {
continue
}
var s *Site
var err error
cfg.Language = lang
// 为每个语言创建一个 site
s, err = newSite(cfg)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
sites = append(sites, s)
}
return sites, nil
}
为每个语言生成一个 Site。
2.2.2. 内容加载
注册回调函数:
// hugolib/site.go
// 初始化
func (s *Site) prepareInits() {
s.init = &siteInit{}
var init lazy.Init
// 回调函数
s.init.prevNext = init.Branch(func() (interface{}, error) {
// 获取 pages
regularPages := s.RegularPages()
for i, p := range regularPages {
np, ok := p.(nextPrevProvider)
if !ok {
continue
}
pos := np.getNextPrev()
if pos == nil {
continue
}
pos.nextPage = nil
pos.prevPage = nil
if i > 0 {
pos.nextPage = regularPages[i-1]
}
if i < len(regularPages)-1 {
pos.prevPage = regularPages[i+1]
}
}
return nil, nil
})
s.init.prevNextInSection = init.Branch(func() (interface{}, error) {
var sections page.Pages
s.home.treeRef.m.collectSectionsRecursiveIncludingSelf(pageMapQuery{Prefix: s.home.treeRef.key}, func(n *contentNode) {
sections = append(sections, n.p)
})
setNextPrev := func(pas page.Pages) {
for i, p := range pas {
np, ok := p.(nextPrevInSectionProvider)
if !ok {
continue
}
pos := np.getNextPrevInSection()
if pos == nil {
continue
}
pos.nextPage = nil
pos.prevPage = nil
if i > 0 {
pos.nextPage = pas[i-1]
}
if i < len(pas)-1 {
pos.prevPage = pas[i+1]
}
}
}
for _, sect := range sections {
treeRef := sect.(treeRefProvider).getTreeRef()
var pas page.Pages
treeRef.m.collectPages(pageMapQuery{Prefix: treeRef.key + cmBranchSeparator}, func(c *contentNode) {
pas = append(pas, c.p)
})
page.SortByDefault(pas)
setNextPrev(pas)
}
// The root section only goes one level down.
treeRef := s.home.getTreeRef()
var pas page.Pages
treeRef.m.collectPages(pageMapQuery{Prefix: treeRef.key + cmBranchSeparator}, func(c *contentNode) {
pas = append(pas, c.p)
})
page.SortByDefault(pas)
setNextPrev(pas)
return nil, nil
})
s.init.menus = init.Branch(func() (interface{}, error) {
s.assembleMenus()
return nil, nil
})
s.init.taxonomies = init.Branch(func() (interface{}, error) {
err := s.pageMap.assembleTaxonomies()
return nil, err
})
}
3. 性能优化细节
3.1. interface 实现约束
代码中有多处使用如下方式在编译时约束 interface 被实现。
var _ cmder = (*newCmd)(nil)
其他开源项目中有也有这种写法的:
var _ cmder = &newCmd{}
var _ cmder = newCmd{}
3.2. 防抖
package debounce
import (
"sync"
"time"
)
// New returns a debounced function that takes another functions as its argument.
// This function will be called when the debounced function stops being called
// for the given duration.
// The debounced function can be invoked with different functions, if needed,
// the last one will win.
func New(after time.Duration) func(f func()) {
d := &debouncer{after: after}
return func(f func()) {
d.add(f)
}
}
type debouncer struct {
mu sync.Mutex
after time.Duration
timer *time.Timer
}
func (d *debouncer) add(f func()) {
d.mu.Lock()
defer d.mu.Unlock()
// 如果正在延时中,取消当前延时,添加新的延时
if d.timer != nil {
d.timer.Stop()
}
d.timer = time.AfterFunc(d.after, f)
}
防抖函数的使用类似 React Hooks。
f := func()
run := debounce.New(f)
run()
在 Istio 源码中,处理 XDS 推流时也会进行防抖处理。
3.2. LIFO 队列
// LIFO 队列,溢出的元素会从顶部移除
// 没有主动删除元素的方法
// EvictingStringQueue is a queue which automatically evicts elements from the head of
// the queue when attempting to add new elements onto the queue and it is full.
// This queue orders elements LIFO (last-in-first-out). It throws away duplicates.
// Note: This queue currently does not contain any remove (poll etc.) methods.
type EvictingStringQueue struct {
size int
vals []string // 储存真实的数据
set map[string]bool // 表示是否已经存在
mu sync.Mutex
}
// NewEvictingStringQueue creates a new queue with the given size.
func NewEvictingStringQueue(size int) *EvictingStringQueue {
return &EvictingStringQueue{size: size, set: make(map[string]bool)}
}
// Add adds a new string to the tail of the queue if it's not already there.
func (q *EvictingStringQueue) Add(v string) {
q.mu.Lock()
// 已经存在
if q.set[v] {
q.mu.Unlock()
return
}
// 数量达到最大限制
if len(q.set) == q.size {
// Full
// 移除了 0 号元素的占位符
delete(q.set, q.vals[0])
// :0 取空数组,1:取不包含第一个元素的其余元素
// 移除了数组 0 号元素
q.vals = append(q.vals[:0], q.vals[1:]...)
}
// 表示存在
q.set[v] = true
// 最新插入的值在数组最后
// 是队列结构
q.vals = append(q.vals, v)
q.mu.Unlock()
}
// Contains returns whether the queue contains v.
func (q *EvictingStringQueue) Contains(v string) bool {
q.mu.Lock()
defer q.mu.Unlock()
return q.set[v]
}
// Peek looks at the last element added to the queue.
func (q *EvictingStringQueue) Peek() string {
q.mu.Lock()
l := len(q.vals)
// 处理边界条件
if l == 0 {
q.mu.Unlock()
return ""
}
// 取最后一个元素
elem := q.vals[l-1]
q.mu.Unlock()
return elem
}
// PeekAll looks at all the elements in the queue, with the newest first.
func (q *EvictingStringQueue) PeekAll() []string {
q.mu.Lock()
vals := make([]string, len(q.vals))
copy(vals, q.vals)
q.mu.Unlock()
// i 从头开始循环 j 从尾循环
// 交换 i j 元素位置
// 数组 reverse
// 最后插入的在最前面
for i, j := 0, len(vals)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
vals[i], vals[j] = vals[j], vals[i]
}
return vals
}
// PeekAllSet returns PeekAll as a set.
func (q *EvictingStringQueue) PeekAllSet() map[string]bool {
all := q.PeekAll()
set := make(map[string]bool)
for _, v := range all {
set[v] = true
}
return set
}
3.3. 同步信号量
golang.org/x/sync/semaphore 扩展同步原语。
3.4. Command
3.4.1. CLI 自动补全
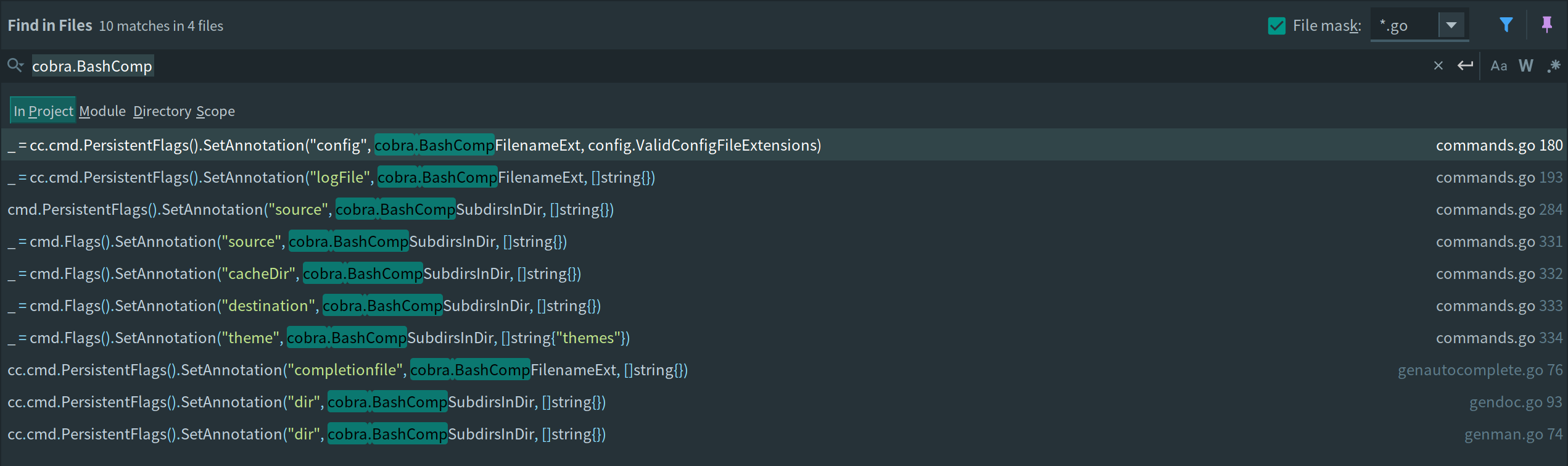
Hugo 的使用方式有两种:
// "-config" flag 自动补全指定后缀文件名
_ = cc.cmd.PersistentFlags().SetAnnotation("config", cobra.BashCompFilenameExt, config.ValidConfigFileExtensions)
// "-source" flag 自动补全子文件夹名
cmd.PersistentFlags().SetAnnotation("source", cobra.BashCompSubdirsInDir, []string{})
3.5. 并发控制
3.5.1. 缓冲通道控制并发
// common/para/para.go
// Package para implements parallel execution helpers.
package para
import (
"context"
"golang.org/x/sync/errgroup"
)
// Workers configures a task executor with the most number of tasks to be executed in parallel.
type Workers struct {
sem chan struct{}
}
// Runner wraps the lifecycle methods of a new task set.
//
// Run wil block until a worker is available or the context is cancelled,
// and then run the given func in a new goroutine.
// Wait will wait for all the running goroutines to finish.
type Runner interface {
Run(func() error)
Wait() error
}
type errGroupRunner struct {
*errgroup.Group
w *Workers
ctx context.Context
}
func (g *errGroupRunner) Run(fn func() error) {
select {
// 分配一个信号, 如果 chan 被关闭则退出
case g.w.sem <- struct{}{}:
case <-g.ctx.Done():
return
}
g.Go(func() error {
err := fn()
// 执行完后消费信号量, 通过缓存通道保证并发执行的协程数量
<-g.w.sem
return err
})
}
// New creates a new Workers with the given number of workers.
func New(numWorkers int) *Workers {
return &Workers{
// 缓冲通道, 并发写入
sem: make(chan struct{}, numWorkers),
}
}
// Start starts a new Runner.
func (w *Workers) Start(ctx context.Context) (Runner, context.Context) {
g, ctx := errgroup.WithContext(ctx)
return &errGroupRunner{
Group: g,
ctx: ctx,
w: w,
}, ctx
}
Playground 测试示例: https://play.golang.org/p/4AJtyVnlSOd
func main() {
w := para.New(10)
runner, _ := w.Start(context.TODO())
runner.Run(func() error {
fmt.Println("fucking")
return nil
})
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
}
3.6. 懒加载
Lazy 包
3.6.1. onceMore
package lazy
import (
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
)
// onceMore is similar to sync.Once.
//
// Additional features are:
// * it can be reset, so the action can be repeated if needed
// * it has methods to check if it's done or in progress
//
type onceMore struct {
mu sync.Mutex
lock uint32
done uint32
}
func (t *onceMore) Do(f func()) {
if atomic.LoadUint32(&t.done) == 1 {
return
}
// f may call this Do and we would get a deadlock.
locked := atomic.CompareAndSwapUint32(&t.lock, 0, 1)
if !locked {
// 没有抢到原子操作
return
}
// 释放原子锁
// defer 是 FILO, 该原子锁会最后才释放
defer atomic.StoreUint32(&t.lock, 0)
// 并发锁, 保证 t.done 值的读取不会产生竞争
t.mu.Lock()
defer t.mu.Unlock()
// Double check
if t.done == 1 {
return
}
defer atomic.StoreUint32(&t.done, 1)
f()
}
func (t *onceMore) InProgress() bool {
return atomic.LoadUint32(&t.lock) == 1
}
func (t *onceMore) Done() bool {
return atomic.LoadUint32(&t.done) == 1
}
func (t *onceMore) ResetWithLock() *sync.Mutex {
t.mu.Lock()
defer atomic.StoreUint32(&t.done, 0)
return &t.mu
}
3.6.2. init
package lazy
import (
"context"
"sync"
"time"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
)
// New creates a new empty Init.
func New() *Init {
return &Init{}
}
// Init holds a graph of lazily initialized dependencies.
type Init struct {
mu sync.Mutex // 并发修改图的锁
prev *Init
children []*Init
init onceMore // 保证只执行一次的锁
out interface{} // 执行结果
err error // 执行错误
f func() (interface{}, error) // 回调函数
}
// Add adds a func as a new child dependency.
func (ini *Init) Add(initFn func() (interface{}, error)) *Init {
if ini == nil {
ini = New()
}
return ini.add(false, initFn)
}
// AddWithTimeout is same as Add, but with a timeout that aborts initialization.
func (ini *Init) AddWithTimeout(timeout time.Duration, f func(ctx context.Context) (interface{}, error)) *Init {
return ini.Add(func() (interface{}, error) {
return ini.withTimeout(timeout, f)
})
}
// Branch creates a new dependency branch based on an existing and adds
// the given dependency as a child.
func (ini *Init) Branch(initFn func() (interface{}, error)) *Init {
if ini == nil {
ini = New()
}
return ini.add(true, initFn)
}
// BranchdWithTimeout is same as Branch, but with a timeout.
func (ini *Init) BranchWithTimeout(timeout time.Duration, f func(ctx context.Context) (interface{}, error)) *Init {
return ini.Branch(func() (interface{}, error) {
return ini.withTimeout(timeout, f)
})
}
// Do initializes the entire dependency graph.
func (ini *Init) Do() (interface{}, error) {
if ini == nil {
panic("init is nil")
}
// 调用 onceMore 库保证只执行一次
ini.init.Do(func() {
// 获取父节点
prev := ini.prev
if prev != nil {
// A branch. Initialize the ancestors.
// 若父节点还没有完成初始化, 并且没有正在执行的回调函数, 执行
if prev.shouldInitialize() {
_, err := prev.Do()
if err != nil {
ini.err = err
return
}
} else if prev.inProgress() {
// Concurrent initialization. The following init func
// may depend on earlier state, so wait.
// 等待一定时间, 若没有执行完, panic
prev.wait()
}
}
// 执行回调函数
if ini.f != nil {
ini.out, ini.err = ini.f()
}
// 循环执行子节点的回调函数
// 为什么不并发执行 ?
for _, child := range ini.children {
if child.shouldInitialize() {
_, err := child.Do()
if err != nil {
ini.err = err
return
}
}
}
})
ini.wait()
return ini.out, ini.err
}
// TODO(bep) investigate if we can use sync.Cond for this.
func (ini *Init) wait() {
var counter time.Duration
for !ini.init.Done() {
counter += 10
if counter > 600000000 {
panic("BUG: timed out in lazy init")
}
time.Sleep(counter * time.Microsecond)
}
}
func (ini *Init) inProgress() bool {
return ini != nil && ini.init.InProgress()
}
// 若 没有注册了回调函数 | 已经完成 | 正在执行, 不进行初始化
func (ini *Init) shouldInitialize() bool {
return !(ini == nil || ini.init.Done() || ini.init.InProgress())
}
// Reset resets the current and all its dependencies.
func (ini *Init) Reset() {
mu := ini.init.ResetWithLock()
defer mu.Unlock()
for _, d := range ini.children {
d.Reset()
}
}
// 添加图的节点
func (ini *Init) add(branch bool, initFn func() (interface{}, error)) *Init {
ini.mu.Lock()
defer ini.mu.Unlock()
// 如果是新建分支
if branch {
return &Init{
f: initFn,
prev: ini, // 父节点
}
}
// 如果是添加子节点
// 如果已经被执行, panic
ini.checkDone()
// 添加子节点
ini.children = append(ini.children, &Init{
f: initFn,
})
// 释放锁
return ini
}
func (ini *Init) checkDone() {
if ini.init.Done() {
panic("init cannot be added to after it has run")
}
}
// callback 函数, 有超时时间
func (ini *Init) withTimeout(timeout time.Duration, f func(ctx context.Context) (interface{}, error)) (interface{}, error) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), timeout)
defer cancel()
// 缓存通道, 防止阻塞
c := make(chan verr, 1)
go func() {
v, err := f(ctx)
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return
default:
c <- verr{v: v, err: err}
}
}()
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return nil, errors.New("timed out initializing value. You may have a circular loop in a shortcode, or your site may have resources that take longer to build than the `timeout` limit in your Hugo config file.")
case ve := <-c:
return ve.v, ve.err
}
}
type verr struct {
v interface{}
err error
}