本文于 2021.05.21 发表于敝司内部,现做部分修订与批注公开发表。
Dkron 是基于 Google 白皮书理论编写的分布式任务调度系统,内部技术利用到了 Serf(Gossip)进行病毒式消息扩散,Raft 进行分布式数据强一致性同步,设计上采用 Server / Agent 模式,只有一个中心调度主节点,其他节点作为工作节点,通过 go-plugin 插件机制定义多种类型、可自由扩展的任务处理器,使用 GRPC 的双向流传输进行任务分发与状态上报,同时使用 net/rpc 进行跨进程调用,还使用高性能 KV 储存 buntdb 的 in-memory 模式缓存与结构化储存任务元数据。
Dkron 可谓是站在了巨人的肩膀上,利用了诸多优秀开源组件,汲取了优秀设计思想实现的产品(官方还运营了商业版本)。
我在将其引入公司落地途中,对其进行了代码审计,本文便是落地过程中的产物之一(学习笔记)。由于 Dkron 涉及到的开源组件较多,光是 Goosip 与 Raft 协议就够复杂了,我抱着学习的心态进行工作,逐渐对这些开源组件有了认知,阅读代码也知道具体的用法是什么样子,有一定的收获。
本文基于 2021.05.19 dkron 最新 master 分支(对应 v3.1.6 版本)代码阅读, 详细源码笔记于 mayocream/dkron review 分支。
1. 架构设计
1.1. 概述
引用 Dkron 官网的表述:
Dkron 是分布式的 Cron 服务,以 Golang 编写,并利用 Raft 协议和 Serf 提供可容错性,可靠性和可伸缩性,同时易于使用与安装。
1.2. 设计思路
Dkron 参考 Google 的分布式 Cron 系统白皮书,实现了与 Google 内部任务系统“相同”的功能。
1.2.1. 可靠性
Running these jobs is facilitated by keeping a file containing timestamps of the last launch for all registered Cron jobs.
Dkron 的 Job 数据结构包含了任务最后一次执行的时间戳:
message Job {
...
// 最后一次执行成功/失败时间戳
NullableTime last_success = 25;
NullableTime last_error = 26;
// 下一次执行时间戳
google.protobuf.Timestamp next = 23;
...
}
To make matters more complicated, failure to launch is acceptable for some Cron jobs but not for others. A garbage collection Cron job scheduled to run every five minutes may be able to skip one launch, but a payroll job scheduled to run once a month probably should not.
一些任务设计上不是幂等的,简单地错误重试会导致严重的问题,任务所有者应有任务执行、重试等操作的控制权。
Dkron 能够让用户控制 Job 的执行、重试次数:
message Job {
...
// 启用/禁用
bool disabled = 11;
// 错误尝试次数
uint32 retries = 13;
// 是否允许同时调度
string concurrency = 16;
...
}
1.2.2. 可伸缩性
If you want to run a service, simply specify which data center it should run in and what it requires — the data center scheduling system (which itself should be reliable) takes care of figuring out which machine or machines to deploy it on, as well as handling machine deaths. Launching a job in a data center then effectively turns into sending one or more RPCs to the data center scheduler.
定时任务分布式地运行,设计上要能够避免集群中一台机器宕机影响。
Dkron 在任务调度和集群通信上定义了“数据中心”,所有的 Dkron 实例可以通过 Gossip 组建集群。但 Dkron 目前只支持同一数据中心下进行任务调度,不支持跨数据中心调度任务。
Dkron 任务调度程序和执行节点通过 RPC 通信。
1.2.3. 状态储存
We have two options: store data externally in a generally available distributed storage, or store a small amount of state as part of the Cron service itself. When designing the distributed Cron, we opted for the second option.
任务执行状态在 Dkron 被视为是与 Server 一体的,Dkron 通过 Raft FSM 在调度集群 Server 之间同步 Job 和 Job 执行历史的数据。社区版本数据储存在内存 KV (Buntdb) 中,Pro 版本支持 etcd 储存。
持久化数据通过 Raft Snapshot 实现。
1.2.4. 任务调度
集群
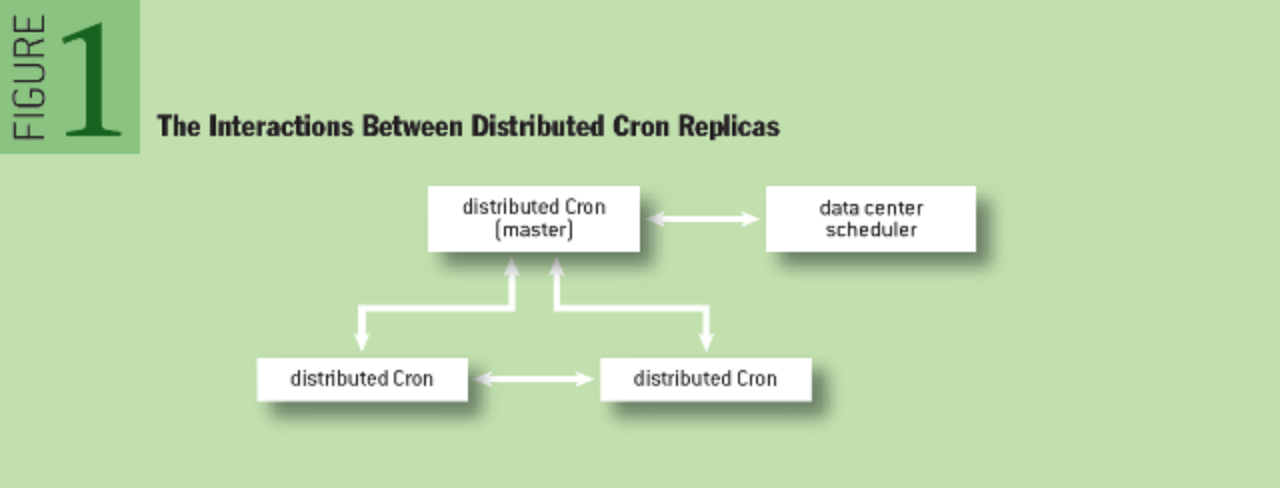
Dkron 中服务器节点分为 Server / Agent,Server 集群负责 Job 的数据存储,Server 中选举出的 Leader 负责任务调度。Server 同时也是 Agent,可以执行 Job。
Dkron 通过 Gossip 组建集群,通过 Raft 选举 Leader,Leader 担当 Scheduler,通过 GRPC 下发 Job 到 Gossip 集群的 Peers 节点执行。当 Leader 节点宕机,会在 Server 集群中选举出新的 Leader。
任务执行
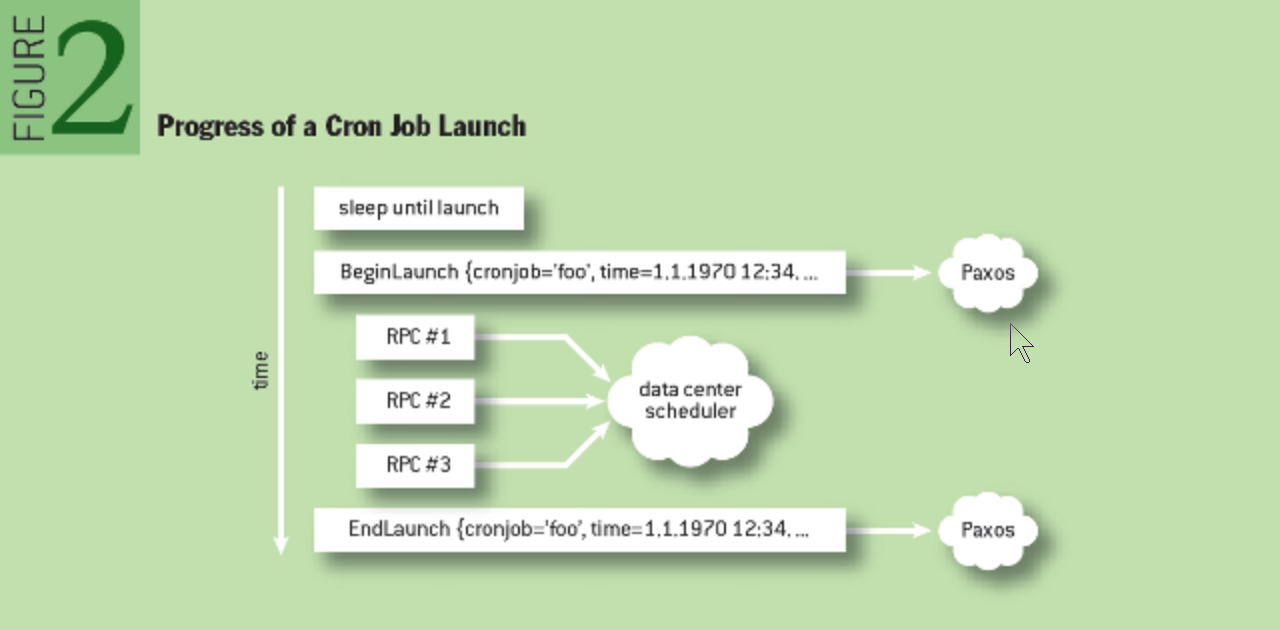
Dkron Job 执行中 Agent 与 Server GRPC 双向流通信,Agent 持续发送任务执行情况,Server 记录任务开始和任务结束时的执行状态,通过 Raft Apply 同步到 Server 集群。
2. 源码分析
2.1. 基本概述
2.1.1. 主要机制
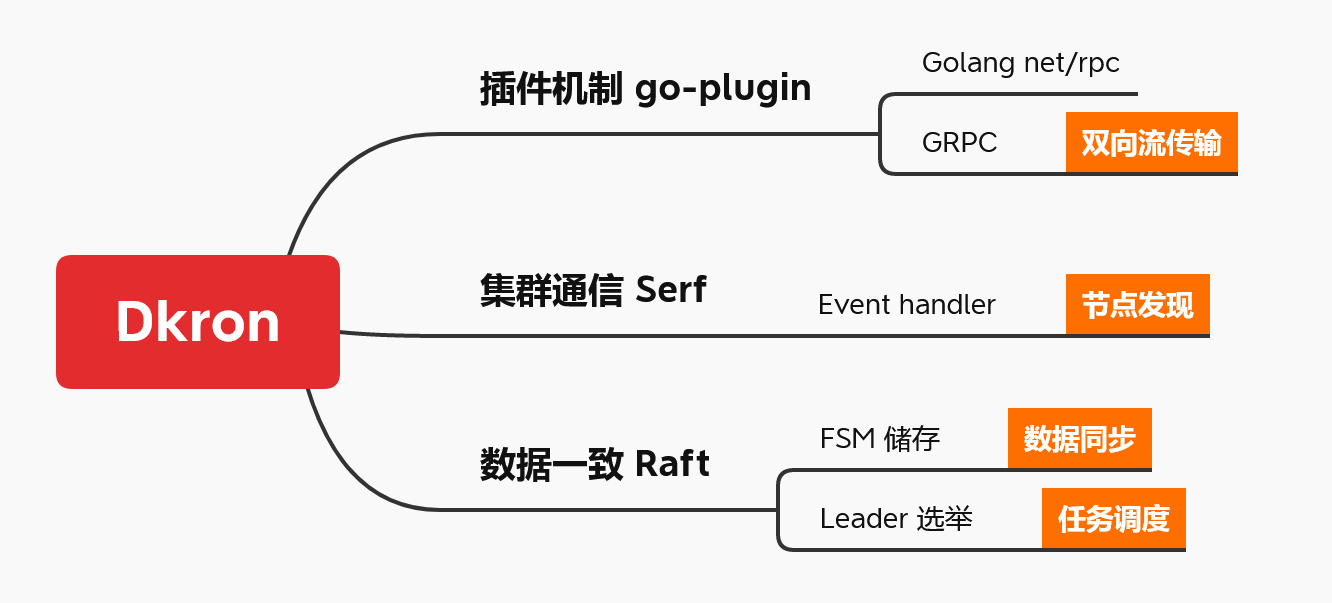
Dkron 主要基于三大机制实现分布式任务调度:
- 通过 Gossip 库 Serf 实现节点发现、集群组建,监听 Gossip Member 变化事件,发现 Server/Agent 的 Peer 通信地址及活跃状态;
- 通过 Raft 实现 Server 集群 Leader 选举,实现 FSM 接口,通过 Raft Log 实现 Server 集群数据同步、数据快照、数据最终一致性;
- 利用 go-plugin 实现插件机制,基于 GRPC 通信 Agent 实时返回任务执行状态。
2.1.2. 目录结构
$ tree -A -L 1
.
# 自带的插件 /Processor 的 main 包
├── builtin
# CLI
├── cmd
# 主要功能实现
├── dkron
├── Dockerfile
# 封装 cron
├── extcron
├── go.mod
├── main.go
# 生成的 pb.go 以及通信逻辑
├── plugin
# 定义 Job 以及通信协议
├── proto
2.2. 组建集群
2.2.1. 节点发现
Dkron 使用 hashicorp/go-discover 进行节点 IP 的自动发现,方便通过云厂商接口、K8s 进行初始化服务发现。用于发现 Peer 节点,进行 Bootstrap 或者 Join 集群。
// dkron/retry_join.go
func (r *retryJoiner) retryJoin(logger *logrus.Entry) error {
...
// 使用 go-discovery 发通过不同的基础设施自动发现 IP
// Copy the default providers, and then add the non-default
providers := make(map[string]discover.Provider)
for k, v := range discover.Providers {
providers[k] = v
}
// 尝试 In-Cluster 方式从 "/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"
// 获取 kubeconfig
// ref: https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/tree/master/examples/in-cluster-client-configuration
// 获取 PodIP 列表
providers["k8s"] = &discoverk8s.Provider{}
disco, err := discover.New(
discover.WithUserAgent(UserAgent()),
discover.WithProviders(providers),
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
attempt := 0
for {
var addrs []string
var err error
for _, addr := range r.addrs {
switch {
// 使用 go-discovery 发现 IP
case strings.Contains(addr, "provider="):
servers, err := disco.Addrs(addr, log.New(logger.Logger.Writer(), "", log.LstdFlags|log.Lshortfile))
if err != nil {
...
} else {
addrs = append(addrs, servers...)
}
default:
ipAddr, err := ParseSingleIPTemplate(addr)
if err != nil {
logger.WithField("addr", addr).WithError(err).Error("agent: Error parsing retry-join ip template")
continue
}
addrs = append(addrs, ipAddr)
}
}
if len(addrs) > 0 {
// Serf 加入集群
n, err := r.join(addrs)
if err == nil {
logger.Infof("agent: Join %s completed. Synced with %d initial agents", r.cluster, n)
return nil
}
}
attempt++
}
}
在 K8s 部署方式中程序通过创建 go-client,请求 K8s API Server 筛选获取一批 Dkron 的 Pod IP。
2.2.2. Gossip 集群
Dkron 使用 hashicorp/serf 库(Gossip 封装)的 Member 事件 Handler,监听集群成员变化事件,进行集群 Peers 的管理。
默认使用 8946 端口进行 Gossip 集群的 Peers 通信。
// dkron/agent.go
// setupSerf is used to create the agent we use
func (a *Agent) setupSerf() (*serf.Serf, error) {
...
serfConfig := serf.DefaultConfig()
serfConfig.Init()
// metadata
serfConfig.Tags = a.config.Tags
serfConfig.Tags["role"] = "dkron"
// 默认 "dc1"
serfConfig.Tags["dc"] = a.config.Datacenter
// 默认 "global"
serfConfig.Tags["region"] = a.config.Region
serfConfig.Tags["version"] = Version
if a.config.Server {
serfConfig.Tags["server"] = strconv.FormatBool(a.config.Server)
}
if a.config.Bootstrap {
serfConfig.Tags["bootstrap"] = "1"
}
if a.config.BootstrapExpect != 0 {
serfConfig.Tags["expect"] = fmt.Sprintf("%d", a.config.BootstrapExpect)
}
// gossip 默认连接环境/连接参数
switch config.Profile {
case "lan":
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig = memberlist.DefaultLANConfig()
case "wan":
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig = memberlist.DefaultWANConfig()
case "local":
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig = memberlist.DefaultLocalConfig()
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown profile: %s", config.Profile)
}
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig.BindAddr = bindIP
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig.BindPort = bindPort
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig.AdvertiseAddr = advertiseIP
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig.AdvertisePort = advertisePort
serfConfig.MemberlistConfig.SecretKey = encryptKey
serfConfig.NodeName = config.NodeName
serfConfig.Tags = config.Tags
if err != nil {
a.logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Create a channel to listen for events from Serf
a.eventCh = make(chan serf.Event, 2048)
serfConfig.EventCh = a.eventCh
// Start Serf
a.logger.Info("agent: Dkron agent starting")
// Create serf first
return serf.Create(serfConfig)
}
hashicorp/memberlist 提供三个默认配置,局域网络的配置 DefaultLANConfig、外网 DefaultWANConfig、本地 DefaultLocalConfig,后两者都是在 DefaultLANConfig 基础上修改,区别是根据网速,调整了Gossip interval、TCP 超时时间等。
// dkron/retry_join.go
func (r *retryJoiner) retryJoin(logger *logrus.Entry) error {
...
if len(addrs) > 0 {
// Serf 加入集群
n, err := r.join(addrs)
if err == nil {
logger.Infof("agent: Join %s completed. Synced with %d initial agents", r.cluster, n)
return nil
}
}
attempt++
time.Sleep(r.interval)
...
}
程序启动后反复尝试加入 Gossip 集群。
2.2.3. 端口复用
Dkron 默认使用 6868 端口作为 Dkron 的 Peers RPC 通信端口。
默认会挂载 GRPC Server 用于服务调用。在节点为 Server 时同时开启 Raft 协议,复用端口。
// StartServer launch a new dkron server process
// 启动 Server
func (a *Agent) StartServer() {
...
// 创建端口复用 cmux
// Create a cmux object.
tcpm := cmux.New(a.listener)
var grpcl, raftl net.Listener
// If TLS config present listen to TLS
if a.TLSConfig != nil {
...
// 默认不启用 TLS
} else {
// 实现 raft.StreamLayer
a.raftLayer = NewRaftLayer(a.logger)
// cmux match grpc 通信
grpcl = tcpm.MatchWithWriters(cmux.HTTP2MatchHeaderFieldSendSettings("content-type", "application/grpc"))
// raft TCP 通信
raftl = tcpm.Match(cmux.Any())
}
// 创建 GRPC Server
if a.GRPCServer == nil {
a.GRPCServer = NewGRPCServer(a, a.logger)
}
// 启动 GRPC Server
if err := a.GRPCServer.Serve(grpcl); err != nil {
a.logger.WithError(err).Fatal("agent: RPC server failed to start")
}
// 绑定 net Listener
if err := a.raftLayer.Open(raftl); err != nil {
a.logger.Fatal(err)
}
// 启动 Raft
if err := a.setupRaft(); err != nil {
a.logger.WithError(err).Fatal("agent: Raft layer failed to start")
}
// Start serving everything
go func() {
// 正式开始 listen
if err := tcpm.Serve(); err != nil {
a.logger.Fatal(err)
}
}()
...
}
使用 soheilhy/cmux 包进行端口复用,读取字节流前 N 字节(Match 规则)匹配 HTTP/2 GRPC 请求。
2.3. Raft 协议
Dkron 使用的是 hashicorp/raft 实现的 Raft 协议。
2.3.1. 集群初始化
创建 Raft
Dkron 可以指定一台节点 Bootstrap,也可以设置 bootstrap-expect 等待集群 Peers 数量达到指定个数,再进行 Raft 集群 Bootstrap。
// 初始化 Raft
func (a *Agent) setupRaft() error {
if a.config.BootstrapExpect > 0 {
if a.config.BootstrapExpect == 1 {
// 进行 bootstrap
a.config.Bootstrap = true
}
}
// 创建 raft transport
// (Raft 节点间的通信通道),节点之间需要通过这个通道来进行日志同步、领导者选举等等
// 方法内部启动协程 listen listener
transport := raft.NewNetworkTransport(a.raftLayer, 3, raftTimeout, logger)
a.raftTransport = transport
config := raft.DefaultConfig()
// Raft performance
// 默认值为 1
raftMultiplier := a.config.RaftMultiplier
if raftMultiplier < 1 || raftMultiplier > 10 {
return fmt.Errorf("raft-multiplier cannot be %d. Must be between 1 and 10", raftMultiplier)
}
config.HeartbeatTimeout = config.HeartbeatTimeout * time.Duration(raftMultiplier)
config.ElectionTimeout = config.ElectionTimeout * time.Duration(raftMultiplier)
config.LeaderLeaseTimeout = config.LeaderLeaseTimeout * time.Duration(a.config.RaftMultiplier)
config.LogOutput = logger
config.LocalID = raft.ServerID(a.config.NodeName)
// Build an all in-memory setup for dev mode, otherwise prepare a full
// disk-based setup.
var logStore raft.LogStore
var stableStore raft.StableStore
var snapshots raft.SnapshotStore
if a.config.DevMode {
...
} else {
var err error
// (快照存储,用来存储节点的快照信息),也就是压缩后的日志数据
snapshots, err = raft.NewFileSnapshotStore(filepath.Join(a.config.DataDir, "raft"), 3, logger)
// Create the BoltDB backend
s, err := raftboltdb.NewBoltStore(filepath.Join(a.config.DataDir, "raft", "raft.db"))
a.raftStore = s
// (稳定存储,用来存储 Raft 集群的节点信息等),比如,当前任期编号、最新投票时的任期编号等
stableStore = s
// 512 size 内存缓存
cacheStore, err := raft.NewLogCache(raftLogCacheSize, s)
if err != nil {
s.Close()
return err
}
// 用来存储 Raft 的日志
logStore = cacheStore
...
}
...
// 参数: 实现了 Storage 的 DB, 默认 nil, logger
// 创建实现 raft FSM 接口
// raft 只是定义了一个接口,最终交给应用层实现。应用层收到 Log 后按 业务需求 还原为 应用数据保存起来
// Raft 启动时 便 Raft.runFSM 起一个goroutine 从 fsmMutateCh channel 消费log ==> FSM.Apply
fsm := newFSM(a.Store, a.ProAppliers, a.logger)
// 创建 raft 节点
rft, err := raft.NewRaft(config, fsm, logStore, stableStore, snapshots, transport)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("new raft: %s", err)
}
// 选举 leader 信号 chan
a.leaderCh = rft.LeaderCh()
a.raft = rft
return nil
}
默认使用 /dkron/raft 目录储存 Raft Log 和快照。使用 hashicorp/raft-boltdb 作为 Raft Log 和 stable 储存,快照使用文件储存。
线上使用情况:Server 运行 7 天每 30s 执行 5 个 Job ,
raft.db大小为 25M,内存占用在 200M 左右。
数据量不大应该不用考虑大量磁盘和内存占用。
创建集群
如果是初始化集群,指定 bootstrap-expect 参数,则会监听 Gossip 集群成员变化,等待 Peers 数量达到预期时,进行 Raft 的 Bootstrap 操作。
如果已存在 Raft 集群,则新的 Server 加入 Raft 集群的成员中。
// dkron/agent.go
// 处理 Serf 事件
func (a *Agent) eventLoop() {
// 只读的 Shutdown channel
serfShutdownCh := a.serf.ShutdownCh()
for {
select {
// Serf event 事件处理
case e := <-a.eventCh:
// 有三种事件 MemberEvent/UserEvent/Query
// 这里只处理 MemberEvent, 只使用 Serf 做集群 member 的管理
// 实际运行时主要的 MemberEvent 事件有 update/failed/join
// 没有使用到自定义 event 以及 query 命令
// Log all member events
if me, ok := e.(serf.MemberEvent); ok {
for _, member := range me.Members {
a.logger.WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"node": a.config.NodeName,
"member": member.Name,
"event": e.EventType(),
}).Debug("agent: Member event")
}
// serfEventHandler is used to handle events from the serf cluster
switch e.EventType() {
case serf.EventMemberJoin:
a.nodeJoin(me)
a.localMemberEvent(me)
case serf.EventMemberLeave, serf.EventMemberFailed:
a.nodeFailed(me)
a.localMemberEvent(me)
case serf.EventMemberReap:
a.localMemberEvent(me)
case serf.EventMemberUpdate, serf.EventUser, serf.EventQuery: // Ignore
default:
a.logger.WithField("event", e.String()).Warn("agent: Unhandled serf event")
}
}
case <-serfShutdownCh:
a.logger.Warn("agent: Serf shutdown detected, quitting")
return
}
}
}
Serf 的事件有三种类型:MemberEvent / UserEvent / Query,Dkron 只处理 MemberEvent,只使用 Serf 做集群 Peers 的管理,没有使用到自定义 event 以及 query 命令。实际运行时主要的 MemberEvent 事件有 member-update / member-failed / member-join / member-reap。
// dkron/serf.go
// maybeBootstrap is used to handle bootstrapping when a new server joins
func (a *Agent) maybeBootstrap() {
...
// 存在 raft commit 日志, 不需要 bootstrap
if index != 0 {
a.config.BootstrapExpect = 0
return
}
// Scan for all the known servers
members := a.serf.Members()
var servers []ServerParts
voters := 0
for _, member := range members {
valid, p := isServer(member)
if !valid {
// 跳过非 dkron server 的 member
continue
}
if p.Region != a.config.Region {
continue
}
...
if valid {
voters++
}
servers = append(servers, *p)
}
// Skip if we haven't met the minimum expect count
if voters < a.config.BootstrapExpect {
return
}
...
for _, server := range servers {
addr := server.Addr.String()
addrs = append(addrs, addr)
id := raft.ServerID(server.ID)
suffrage := raft.Voter // 允许仲裁的角色
peer := raft.Server{
ID: id,
Address: raft.ServerAddress(addr),
Suffrage: suffrage,
}
configuration.Servers = append(configuration.Servers, peer)
}
// raft 集群初始化
future := a.raft.BootstrapCluster(configuration)
if err := future.Error(); err != nil {
a.logger.WithError(err).Error("agent: failed to bootstrap cluster")
}
// Bootstrapping complete, or failed for some reason, don't enter this again
a.config.BootstrapExpect = 0
}
Raft 集群初始化的条件:
- 没有 Commit 日志;
- Server 集群达到 expect 的数量;
- 属于同一 region
加入节点
若 Raft 集群已存在,则 Leader 节点接收到 Serf Member 加入 Gossip 集群的事件时,进行 Raft 节点 Join 的逻辑:
// dkron/serf.go
func (a *Agent) localMemberEvent(me serf.MemberEvent) {
// 只有 Leader 进行操作
if !a.config.Server || !a.IsLeader() {
return
}
for _, m := range me.Members {
select {
// 加入重新同步的 chan
case a.reconcileCh <- m:
default:
}
}
}
// reconcileCh 触发 reconcile 执行
func (a *Agent) reconcile() error {
members := a.serf.Members()
for _, member := range members {
if err := a.reconcileMember(member); err != nil {
return err
}
}
return nil
}
// dkron/leader.go
func (a *Agent) reconcileMember(member serf.Member) error {
// 判断是否在一个 region, 是否是 Server
valid, parts := isServer(member)
if !valid || parts.Region != a.config.Region {
return nil
}
var err error
switch member.Status {
case serf.StatusAlive:
err = a.addRaftPeer(member, parts)
case serf.StatusLeft:
err = a.removeRaftPeer(member, parts)
}
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
// dkron/leader.go
func (a *Agent) addRaftPeer(m serf.Member, parts *ServerParts) error {
...
// 获取 raft peers
for _, server := range configFuture.Configuration().Servers {
// 要加入的 server 已存在于 raft peers 中, 先移除再添加
if server.Address == raft.ServerAddress(addr) || server.ID == raft.ServerID(parts.ID) {
...
future := a.raft.RemoveServer(server.ID, 0, 0)
...
}
}
// 添加一个 raft peer
switch {
case minRaftProtocol >= 3:
addFuture := a.raft.AddVoter(raft.ServerID(parts.ID), raft.ServerAddress(addr), 0, 0)
if err := addFuture.Error(); err != nil {
a.logger.WithError(err).Error("dkron: failed to add raft peer")
return err
}
}
return nil
}
2.3.2. FSM
内存 DB
Dkron 使用内存 KV tidwall/buntdb 储存 Job 及执行历史记录。
// dkron/storage.go
// Storage is the interface that should be used by any
// storage engine implemented for dkron. It contains the
// minumum set of operations that are needed to have a working
// dkron store.
type Storage interface {
SetJob(job *Job, copyDependentJobs bool) error
DeleteJob(name string) (*Job, error)
SetExecution(execution *Execution) (string, error)
SetExecutionDone(execution *Execution) (bool, error)
GetJobs(options *JobOptions) ([]*Job, error)
GetJob(name string, options *JobOptions) (*Job, error)
GetExecutions(jobName string, opts *ExecutionOptions) ([]*Execution, error)
GetExecutionGroup(execution *Execution, opts *ExecutionOptions) ([]*Execution, error)
GetGroupedExecutions(jobName string, opts *ExecutionOptions) (map[int64][]*Execution, []int64, error)
Shutdown() error
Snapshot(w io.WriteCloser) error
Restore(r io.ReadCloser) error
}
store 实现了 Storage 接口,使用的是 buntdb:
// dkron/store.go
// NewStore creates a new Storage instance.
// 创建基于内存的 buntdb
func NewStore(logger *logrus.Entry) (*Store, error) {
db, err := buntdb.Open(":memory:")
db.CreateIndex("name", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("name"))
db.CreateIndex("started_at", executionsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("started_at"))
db.CreateIndex("finished_at", executionsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("finished_at"))
db.CreateIndex("attempt", executionsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("attempt"))
db.CreateIndex("displayname", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("displayname"))
db.CreateIndex("schedule", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("schedule"))
db.CreateIndex("success_count", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("success_count"))
db.CreateIndex("error_count", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("error_count"))
db.CreateIndex("last_success", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("last_success"))
db.CreateIndex("last_error", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("last_error"))
db.CreateIndex("next", jobsPrefix+":*", buntdb.IndexJSON("next"))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
store := &Store{
db: db,
lock: &sync.Mutex{},
logger: logger,
}
return store, nil
}
官方的 Pro 版本实现的 etcd 储存,可能是实现了 Storage 的另一个实例,或者是在 Raft FSM 进行了额外的处理执行外部数据库同步。
实现 FSM 接口
Raft FSM 接口:
// FSM provides an interface that can be implemented by
// clients to make use of the replicated log.
type FSM interface {
// Apply log is invoked once a log entry is committed.
// It returns a value which will be made available in the
// ApplyFuture returned by Raft.Apply method if that
// method was called on the same Raft node as the FSM.
Apply(*Log) interface{}
// Snapshot is used to support log compaction. This call should
// return an FSMSnapshot which can be used to save a point-in-time
// snapshot of the FSM. Apply and Snapshot are not called in multiple
// threads, but Apply will be called concurrently with Persist. This means
// the FSM should be implemented in a fashion that allows for concurrent
// updates while a snapshot is happening.
Snapshot() (FSMSnapshot, error)
// Restore is used to restore an FSM from a snapshot. It is not called
// concurrently with any other command. The FSM must discard all previous
// state.
Restore(io.ReadCloser) error
}
Apply 函数会在从 Log 载入一条数据的时候被调用。Leader 会调用 Apply 进行数据同步。
// dkron/fsm.go
type dkronFSM struct {
store Storage
// proAppliers holds the set of pro only LogAppliers
proAppliers LogAppliers
logger *logrus.Entry
}
// 创建/同步一条 Log 到 state
func (d *dkronFSM) Apply(l *raft.Log) interface{} {
buf := l.Data
msgType := MessageType(buf[0])
switch msgType {
case SetJobType:
return d.applySetJob(buf[1:])
case DeleteJobType:
return d.applyDeleteJob(buf[1:])
case ExecutionDoneType:
return d.applyExecutionDone(buf[1:])
case SetExecutionType:
return d.applySetExecution(buf[1:])
}
// Dkron Pro 版本额外的操作, 可能在此处执行外部数据库同步
if applier, ok := d.proAppliers[msgType]; ok {
return applier(buf[1:], l.Index)
}
return nil
}
实现的快照和恢复方法,使用 buntdb 的 load/save:
// dkron/fsm.go
// FSM 的快照和恢复方法,使用 buntdb 的 load/save 方法。
// Snapshot returns a snapshot of the key-value store. We wrap
// the things we need in dkronSnapshot and then send that over to Persist.
// Persist encodes the needed data from dkronSnapshot and transport it to
// Restore where the necessary data is replicated into the finite state machine.
// This allows the consensus algorithm to truncate the replicated log.
func (d *dkronFSM) Snapshot() (raft.FSMSnapshot, error) {
return &dkronSnapshot{store: d.store}, nil
}
// Restore stores the key-value store to a previous state.
func (d *dkronFSM) Restore(r io.ReadCloser) error {
defer r.Close()
return d.store.Restore(r)
}
type dkronSnapshot struct {
store Storage
}
func (d *dkronSnapshot) Persist(sink raft.SnapshotSink) error {
if err := d.store.Snapshot(sink); err != nil {
sink.Cancel()
return err
}
// Close the sink.
if err := sink.Close(); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
func (d *dkronSnapshot) Release() {}
数据格式
通过 Raft Log (Bytes) 储存的数据格式为:
// dkron/grpc.go
// Proto 转换成 Bytes
func Encode(t MessageType, msg interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
var buf bytes.Buffer
buf.WriteByte(uint8(t))
m, err := pb.Marshal(msg.(pb.Message))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
_, err = buf.Write(m)
return buf.Bytes(), err
}
首个字节标记 Message 的类型,后续为 Protobuf 序列化后的结果。
2.4. 插件机制
2.4.1. 概述
插件机制优先于任务调度本身进行分析,因为任务调度依赖于插件的通信机制。
Dkron 插件使用 hashicorp/go-plugin 实现,简而概之,通过两种 RPC 方式(netrpc / GRPC)客户端与插件监听的端口进行通信,插件与主程序分离,作为插件机制。
引用 go-plugin 项目的说明:
Shared libraries have one major advantage over our system which is much higher performance. In real world scenarios across our various tools, we've never required any more performance out of our plugin system and it has seen very high throughput, so this isn't a concern for us at the moment.
Golang 出的基于链接库(.so)的插件机制还不成熟,并且 go-plugin 已经在大量软件中运用多年,对比起来前者没有优势,go-plugin 的考量在于性能对于插件机制来说不是首要的。
这里说一句,其他 Golang 的 HTTP 服务器例如 Traefik、Caddy 的插件机制都是需要修改源代码,自行增加包实现 Golang Interface,重新进行编译实现的,这种侵入性更大,但是性能更好。
Golang 官方的插件机制到目前还不支持 Windows,高性能的 WASM Golang 运行时库(用作 WASM 插件机制) wasmerio/wasmer-go 目前也不支持 Windows。
2.4.2. 加载插件
Dkron 默认会在一些目录查找插件的二进制文件:
// cmd/plugins.go
func (p *Plugins) DiscoverPlugins() error {
p.Processors = make(map[string]dkplugin.Processor)
p.Executors = make(map[string]dkplugin.Executor)
// Look in /etc/dkron/plugins
// 匹配目录下的文件列表
processors, err := plugin.Discover("dkron-processor-*", filepath.Join("/etc", "dkron", "plugins"))
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Look in /etc/dkron/plugins
executors, err := plugin.Discover("dkron-executor-*", filepath.Join("/etc", "dkron", "plugins"))
if err != nil {
return err
}
exePath, err := osext.Executable()
if err != nil {
logrus.WithError(err).Error("Error loading exe directory")
} else {
// 从当前 agent 执行目录查找,同目录的可执行文件
// 默认执行目录为 /opt/local/dkron/
// 若我们需要添加自定义插件, 将编译后的二进制文件放入同目录即可
p, err := plugin.Discover("dkron-processor-*", filepath.Dir(exePath))
if err != nil {
return err
}
processors = append(processors, p...)
e, err := plugin.Discover("dkron-executor-*", filepath.Dir(exePath))
if err != nil {
return err
}
executors = append(executors, e...)
}
// pluginFactory
// 创建运行时
for _, file := range processors {
// 文件名按 "-" 分隔,取最后一个元素
// 问题点: 插件名不支持带 "-"
pluginName, ok := getPluginName(file)
if !ok {
continue
}
raw, err := p.pluginFactory(file, dkplugin.ProcessorPluginName)
if err != nil {
return err
}
p.Processors[pluginName] = raw.(dkplugin.Processor)
}
...
return nil
}
2.4.3. 插件实现
Dkron 封装的 Plugin 结构, 规定可以有 processor 或 executor 两个插件。
// PluginMap should be used by clients for the map of plugins.
// Dkron 封装的 Plugin 结构, 规定可以有 processor 或 executor 两个插件
var PluginMap = map[string]plugin.Plugin{
"processor": &ProcessorPlugin{},
"executor": &ExecutorPlugin{},
}
构建插件
// cmd/plugins.go
// 创建 Plugin Client
func (p *Plugins) pluginFactory(path string, pluginType string) (interface{}, error) {
var config plugin.ClientConfig
// 可执行文件
config.Cmd = exec.Command(path)
// handshake 配置是 client 与 server 约定的 TOKEN,
// 不通过环境变量包含同样的 TOKEN 则无法启动 plugin 程序.
// 具体查看 go-plugin 项目 https://github.com/mayocream/go-plugin/blob/044aadd925bf9f027cb301b2af9bc6b60775dd22/server.go#L248
config.HandshakeConfig = dkplugin.Handshake
// go-plugin 包会在 NewClient 的时候储存 Client 的指针,
// 能够调用 cleanClients 统一 Kill 所有的 Client
config.Managed = true
// 定义一个二进制所能包含的不同插件
config.Plugins = dkplugin.PluginMap
config.SyncStdout = os.Stdout
config.SyncStderr = os.Stderr
switch pluginType {
case dkplugin.ProcessorPluginName:
// processor 使用 golang net/rpc 进行通信
config.AllowedProtocols = []plugin.Protocol{plugin.ProtocolNetRPC}
case dkplugin.ExecutorPluginName:
// executor 使用 gprc 进行通信
config.AllowedProtocols = []plugin.Protocol{plugin.ProtocolGRPC}
}
// 初始化客户端
client := plugin.NewClient(&config)
// go-plugin Client() 会用 exec.Start 启动 plugin server,
// 创建 rpc client, 这个库将连接复用, 以及 rpc/grpc service 挂载
// 等细节屏蔽了, 开发者只要创建业务逻辑 Interface 并实现 plugin.Plguin 的
// Serve/Client 方法就能够进行 rpc 通信
rpcClient, err := client.Client()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 调用指定的 service
raw, err := rpcClient.Dispense(pluginType)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return raw, nil
}
运行插件
// go-plugin 插件 start 函数
func (c *Client) Start() (addr net.Addr, err error) {
...
// 启动的环境变量
env := []string{
fmt.Sprintf("%s=%s", c.config.MagicCookieKey, c.config.MagicCookieValue),
fmt.Sprintf("PLUGIN_MIN_PORT=%d", c.config.MinPort),
fmt.Sprintf("PLUGIN_MAX_PORT=%d", c.config.MaxPort),
fmt.Sprintf("PLUGIN_PROTOCOL_VERSIONS=%s", strings.Join(versionStrings, ",")),
}
cmd := c.config.Cmd
cmd.Env = append(cmd.Env, os.Environ()...)
cmd.Env = append(cmd.Env, env...)
cmd.Stdin = os.Stdin
// pipe 读取 std 输出
cmdStdout, err := cmd.StdoutPipe()
cmdStderr, err := cmd.StderrPipe()
// 启动二进制程序
err = cmd.Start()
if err != nil {
return
}
...
// 读取插件执行的 Output
linesCh := make(chan string)
c.clientWaitGroup.Add(1)
go func() {
defer c.clientWaitGroup.Done()
defer close(linesCh)
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(cmdStdout)
for scanner.Scan() {
linesCh <- scanner.Text()
}
}()
...
return
}
2.4.4. 插件通信
插件通信数据结构
message ExecuteRequest {
string job_name = 1;
map<string, string> config = 2;
uint32 status_server = 3;
}
message ExecuteResponse {
bytes output = 1;
string error = 2;
}
service Executor {
rpc Execute (ExecuteRequest) returns (ExecuteResponse);
}
message StatusUpdateRequest {
bytes output = 2;
bool error = 3;
}
message StatusUpdateResponse {
int64 r = 1;
}
service StatusHelper {
rpc Update(StatusUpdateRequest) returns (StatusUpdateResponse);
}
GRPC 双向流通信
// Here is the gRPC client that GRPCClient talks to.
type ExecutorClient struct {
// This is the real implementation
client types.ExecutorClient
broker *plugin.GRPCBroker
}
// ref: https://github.com/distribworks/dkron/pull/719
// 实现执行时实时传输 output, 双向流
func (m *ExecutorClient) Execute(args *types.ExecuteRequest, cb StatusHelper) (*types.ExecuteResponse, error) {
// This is where the magic conversion to Proto happens
statusHelperServer := &GRPCStatusHelperServer{Impl: cb}
var s *grpc.Server
serverFunc := func(opts []grpc.ServerOption) *grpc.Server {
s = grpc.NewServer(opts...)
types.RegisterStatusHelperServer(s, statusHelperServer)
return s
}
brokerID := m.broker.NextId()
go m.broker.AcceptAndServe(brokerID, serverFunc)
args.StatusServer = brokerID
r, err := m.client.Execute(context.Background(), args)
s.Stop()
return r, err
}
目前线上出现过 rpc: transport is closing 的错误,是 GRPC 通信的错误,推测在插件通信的该部分出现错误。
2.5. 任务调度
2.5.1. 概述
Dkron Server 中为 Raft Leader 的服务器成为调度服务器,负责定时任务的分发。
- 通过 GRPC 调用下发任务到 agent 节点,Agent 执行任务并通过 GRPC 流实时返回输出;
- 执行完 Job 后 Leader 通过 Raft Apply 储存 Job 执行记录到各 Server 节点。
2.5.2. cron 封装
Dkron 基于 robfig/cron 增加了 @at 时间定义,允许指定只允许一次的定时任务。
// extcron/extparser.go
// NewParser creates an ExtParser instance
// 启用 second 字段
func NewParser() cron.ScheduleParser {
return ExtParser{cron.NewParser(cron.Second | cron.Minute | cron.Hour | cron.Dom | cron.Month | cron.Dow | cron.Descriptor)}
}
// Parse parses a cron schedule specification. It accepts the cron spec with
// mandatory seconds parameter, descriptors and the custom descriptors
// "@at <date>" and "@manually".
// 添加了自定义解析的部分
func (p ExtParser) Parse(spec string) (cron.Schedule, error) {
if spec == "@manually" {
return At(time.Time{}), nil
}
const at = "@at "
if strings.HasPrefix(spec, at) {
date, err := time.Parse(time.RFC3339, spec[len(at):])
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to parse date %s: %s", spec, err)
}
return At(date), nil
}
// It's not a dkron specific spec: Let the regular cron schedule parser have it
return p.parser.Parse(spec)
}
2.5.3. 数据一致性
// dkron/leader.go
// 处理变成 leader 事件
func (a *Agent) leaderLoop(stopCh chan struct{}) {
RECONCILE:
...
// Apply a raft barrier to ensure our FSM is caught up
start := time.Now()
barrier := a.raft.Barrier(barrierWriteTimeout)
if err := barrier.Error(); err != nil {
a.logger.WithError(err).Error("dkron: failed to wait for barrier")
goto WAIT
}
...
}
变成 Leader 后调用 raft.Barrier 确保 FSM 同步到最新状态。
2.5.4. 任务下发
启动任务调度
// dkron/scheduler.go
// 启动调度器
func (s *Scheduler) Start(jobs []*Job, agent *Agent) error {
s.Cron = cron.New(cron.WithParser(extcron.NewParser()))
for _, job := range jobs {
job.Agent = agent
// 添加所有 Job
s.AddJob(job)
}
// 开始定时执行
s.Cron.Start()
s.Started = true
schedulerStarted.Set(1)
return nil
}
添加单个 Job 到 cron 定时触发:
// dkron/scheduler.go
// AddJob Adds a job to the cron scheduler
// 调度器添加 Job
func (s *Scheduler) AddJob(job *Job) error {
// Check if the job is already set and remove it if exists
if _, ok := s.EntryJobMap.Load(job.Name); ok {
s.RemoveJob(job)
}
if job.Disabled || job.ParentJob != "" {
return nil
}
...
// 为 cron 添加一个 job
// Job 的 Run 是 cron 触发的执行方法
id, err := s.Cron.AddJob(schedule, job)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 储存 cron 的 id
s.EntryJobMap.Store(job.Name, id)
...
return nil
}
触发任务调度
// dkron/job.go
// job 的 run 方法实现 cron.Job 接口
func (j *Job) Run() {
// Check if it's runnable
if j.isRunnable(j.logger) {
...
cronInspect.Set(j.Name, j)
// Simple execution wrapper
ex := NewExecution(j.Name)
// 触发调度运行 Job
if _, err := j.Agent.Run(j.Name, ex); err != nil {
j.logger.WithError(err).Error("job: Error running job")
}
}
}
isRunnable 检查任务是否被禁止,同时通过 GRPC 查询所有 Agent 当前正在执行的任务,是否有相同的 JobName,如果“不允许并发调度”则停止本次调度。
任务分发到 Agent
注意:Dkron 调度会将任务调度到所有符合 tags 的、同一 region 的节点(Serf Members)上。
// dkron/run.go
// 调度运行 Job -> 分发到 agent 执行任务
func (a *Agent) Run(jobName string, ex *Execution) (*Job, error) {
job, err := a.Store.GetJob(jobName, nil)
...
// In case the job is not a child job, compute the next execution time
if job.ParentJob == "" {
// 获取 cron.Entry
if e, ok := a.sched.GetEntry(jobName); ok {
// 获取下一次执行时间
job.Next = e.Next
// 同步 job 数据
if err := a.applySetJob(job.ToProto()); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("agent: Run error storing job %s before running: %w", jobName, err)
}
} else {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("agent: Run error retrieving job: %s from scheduler", jobName)
}
}
// In the first execution attempt we build and filter the target nodes
// but we use the existing node target in case of retry.
var filterMap map[string]string
if ex.Attempt <= 1 {
filterMap, _, err = a.processFilteredNodes(job)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("run error processing filtered nodes: %w", err)
}
} else {
// In case of retrying, find the rpc address of the node or return with an error
// 重试使用同样的 Node 执行
var addr string
for _, m := range a.serf.Members() {
if ex.NodeName == m.Name {
if m.Status == serf.StatusAlive {
addr = m.Tags["rpc_addr"]
} else {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("retry node is gone: %s for job %s", ex.NodeName, ex.JobName)
}
}
}
filterMap = map[string]string{ex.NodeName: addr}
}
...
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for _, v := range filterMap {
// Call here client GRPC AgentRun
wg.Add(1)
go func(node string, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer wg.Done()
// 这里真正调用 GRPC 到 agent 执行
err := a.GRPCClient.AgentRun(node, job.ToProto(), ex.ToProto())
if err != nil {
...
}
}(v, &wg)
}
// 等待所有节点执行完
wg.Wait()
return job, nil
}
Server 对执行状态的处理:
- GRPC 通信开始,Agent 接收到任务;
- GRPC 结束,Agent 执行完成(成功或失败)任务;
// dkron/grpc_client.go
// Dkron server 调用此方法通过 GRPC 下发 Job 到 server/agent 执行
func (grpcc *GRPCClient) AgentRun(addr string, job *proto.Job, execution *proto.Execution) error {
var conn *grpc.ClientConn
// (MAYO): remove string type wrap
conn, err := grpcc.Connect(addr)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer conn.Close()
// Streaming call
a := proto.NewAgentClient(conn)
stream, err := a.AgentRun(context.Background(), &proto.AgentRunRequest{
Job: job,
Execution: execution,
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
var first bool
for {
// 读取 GRPC 流
ars, err := stream.Recv()
// Stream ends
if err == io.EOF {
// 任务执行结束, 发送 done 命令给 leader 持久化储存
addr := grpcc.agent.raft.Leader()
if err := grpcc.ExecutionDone(string(addr), NewExecutionFromProto(execution)); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
// Error received from the stream
if err != nil {
// At this point the execution status will be unknown, set the FinshedAt time and an explanatory message
execution.FinishedAt = ptypes.TimestampNow()
execution.Output = []byte(err.Error())
grpcc.logger.WithError(err).Error(ErrBrokenStream)
addr := grpcc.agent.raft.Leader()
if err := grpcc.ExecutionDone(string(addr), NewExecutionFromProto(execution)); err != nil {
return err
}
return err
}
// Registers an active stream
grpcc.agent.activeExecutions.Store(ars.Execution.Key(), ars.Execution)
execution = ars.Execution
defer grpcc.agent.activeExecutions.Delete(execution.Key())
// Store the received execution in the raft log and store
if !first {
// 储存执行状态
if err := grpcc.SetExecution(ars.Execution); err != nil {
return err
}
first = true
}
}
}
Agent 任务执行
任务执行过程:
- 实时发送执行情况到 Server;
- Server 宕机,切换一个 Server 发送最终状态;
// dkron/grpc_agent.go
// Dkron agent 执行任务, GRPC 客户端推流
func (as *AgentServer) AgentRun(req *types.AgentRunRequest, stream types.Agent_AgentRunServer) error {
job := req.Job
execution := req.Execution
// buffer 创建, 储存执行输出
output, _ := circbuf.NewBuffer(maxBufSize)
var success bool
jex := job.Executor
exc := job.ExecutorConfig
execution.StartedAt = ptypes.TimestampNow()
execution.NodeName = as.agent.config.NodeName
// 发送执行前状态
if err := stream.Send(&types.AgentRunStream{
Execution: execution,
}); err != nil {
return err
}
...
// Check if executor exists
// 找到对应的执行插件
if executor, ok := as.agent.ExecutorPlugins[jex]; ok {
as.logger.WithField("plugin", jex).Debug("grpc_agent: calling executor plugin")
runningExecutions.Store(execution.GetGroup(), execution)
// go-plugin grpc 调用执行
out, err := executor.Execute(&types.ExecuteRequest{
JobName: job.Name,
Config: exc,
// callback, 将执行输出结果赋值到 output, 通过 stream 发送给服务端
// ref: https://github.com/distribworks/dkron/pull/719
}, &statusAgentHelper{
stream: stream,
execution: execution,
})
...
if out != nil {
output.Write(out.Output)
}
} else {
...
output.Write([]byte("grpc_agent: Specified executor is not present"))
}
// 执行完成
execution.FinishedAt = ptypes.TimestampNow()
execution.Success = success
execution.Output = output.Bytes()
runningExecutions.Delete(execution.GetGroup())
// 发送最终状态
if err := stream.Send(&types.AgentRunStream{
Execution: execution,
}); err != nil {
// 有可能 server 没能接收到最后执行状态
...
// TCP 连接筛选一个 server
rpcServer, err := as.agent.checkAndSelectServer()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 调用执行完成
return as.agent.GRPCClient.ExecutionDone(rpcServer, NewExecutionFromProto(execution))
}
return nil
}
任务执行后处理
Job 执行完成后处理:
- 必须为 Leader 进行数据持久化;
- 通过 Raft Apply 同步 Server 间执行记录;
- 错误重试,再次进行任务调度;
- 执行 Job 定义中依赖的 Job。
// dkron/grpc.go
// 执行完成, 进行后续处理
func (grpcs *GRPCServer) ExecutionDone(ctx context.Context, execDoneReq *proto.ExecutionDoneRequest) (*proto.ExecutionDoneResponse, error) {
...
if !grpcs.agent.IsLeader() {
addr := grpcs.agent.raft.Leader()
// 如果我不是 leader , 将请求发给 leader 执行
grpcs.agent.GRPCClient.ExecutionDone(string(addr), NewExecutionFromProto(execDoneReq.Execution))
return nil, ErrNotLeader
}
// This is the leader at this point, so process the execution, encode the value and apply the log to the cluster.
// Get the defined output types for the job, and call them
job, err := grpcs.agent.Store.GetJob(execDoneReq.Execution.JobName, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 执行 processor, 不需要双向通信
// 由此推测 exector 使用 grpc 执行是需要 GRPC 双向流
pbex := *execDoneReq.Execution
for k, v := range job.Processors {
if processor, ok := grpcs.agent.ProcessorPlugins[k]; ok {
v["reporting_node"] = grpcs.agent.config.NodeName
pbex = processor.Process(&plugin.ProcessorArgs{Execution: pbex, Config: v})
} else {
...
}
}
// 同步集群状态
execDoneReq.Execution = &pbex
cmd, err := Encode(ExecutionDoneType, execDoneReq)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
af := grpcs.agent.raft.Apply(cmd, raftTimeout)
if err := af.Error(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Retrieve the fresh, updated job from the store to work on stored values
job, err = grpcs.agent.Store.GetJob(job.Name, nil)
if err != nil {
grpcs.logger.WithError(err).WithField("job", execDoneReq.Execution.JobName).Error("grpc: Error retrieving job from store")
return nil, err
}
// 任务执行重试
execution := NewExecutionFromProto(&pbex)
if !execution.Success && uint(execution.Attempt) < job.Retries+1 {
execution.Attempt++
// Keep all execution properties intact except the last output
execution.Output = ""
...
if _, err := grpcs.agent.Run(job.Name, execution); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &proto.ExecutionDoneResponse{
From: grpcs.agent.config.NodeName,
Payload: []byte("retry"),
}, nil
}
exg, err := grpcs.agent.Store.GetExecutionGroup(execution,
&ExecutionOptions{
Timezone: job.GetTimeLocation(),
},
)
if err != nil {
...
return nil, err
}
...
// 执行依赖的任务
if len(job.DependentJobs) > 0 && job.Status == StatusSuccess {
for _, djn := range job.DependentJobs {
dj, err := grpcs.agent.Store.GetJob(djn, nil)
dj.Agent = grpcs.agent
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
}
return &proto.ExecutionDoneResponse{
From: grpcs.agent.config.NodeName,
Payload: []byte("saved"),
}, nil
}
2.6. 学习笔记
2.6.1. Serf CLI
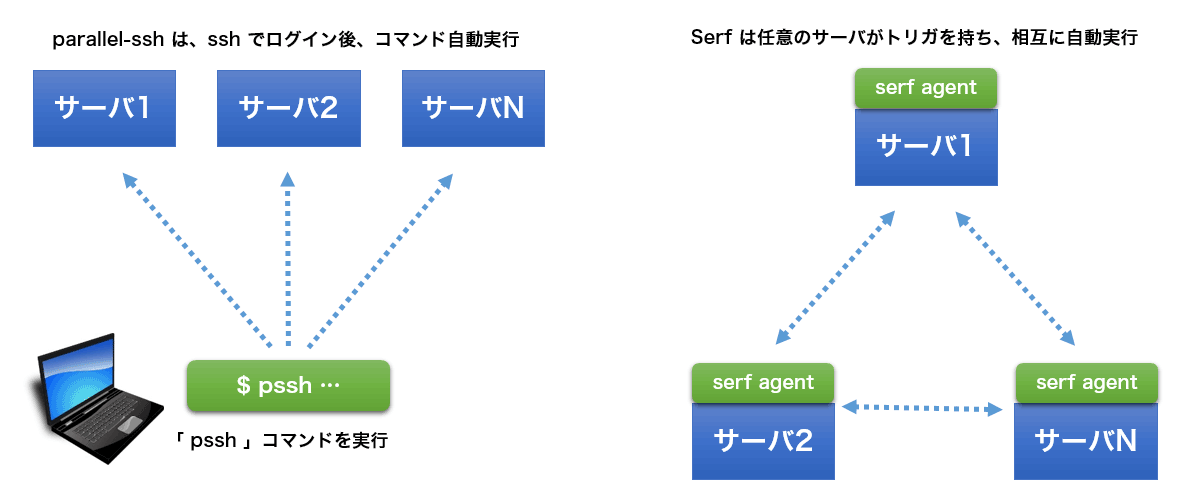
Serf 官方文档的示例主要是分布式运行脚本,通过启动在多个服务器上启动 serf agent(CLI 命令)。
通过配置 Event handler 参数启动:
$ serf agent -event-handler=query:ssh=/bin/bash
发送 Query 命令就可以执行程序了:
$ serf query ssh uptime
Query 'ssh' dispatched
Ack from 'node1.pocketstudio.net'
Ack from 'node2.pocketstudio.net'
Response from 'node2.pocketstudio.net': 05:25:34 up 21:31, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
Total Acks: 2
Total Responses: 1
另外 Consul 的 go.mod 里也引用了 Serf 包。