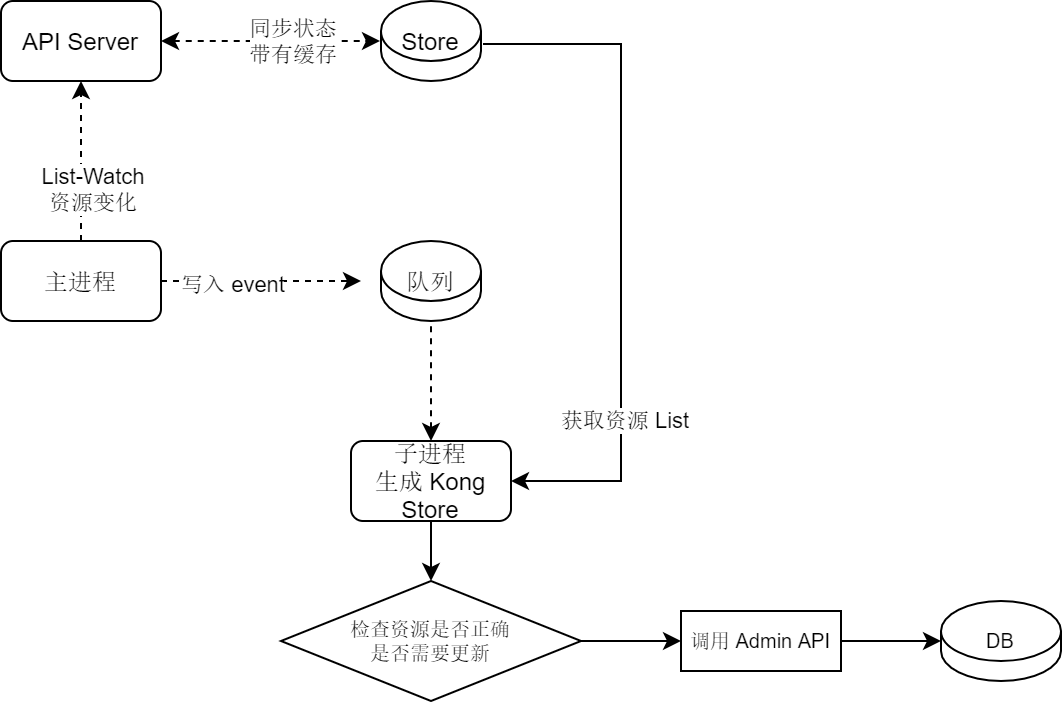
该程序启动后有以下主要步骤:
- 从命令行和环境变量解析入参 (# flags.go)
- 尝试与 Kubernetes API Server 建立连接 (# func createApiserverClient)
- 与 Kong Admin API 通信 (# func kong.NewClient)
- 创建监听资源变化的 Informer
- 创建资源锁竞争选举 Leader (# election.go)
- 队列定时执行同步函数
下面会对其中关键步骤进行解析。
1. 目录结构
├───cli
│ └───ingress-controller
│ flags.go // 参数解析
│ main.go
│ util.go
│ version.go
├───internal
│ ├───admission // Validation Admission Webhook 相关
│ │
│ └───ingress
│ ├───annotations
│ │ annotations.go // 解析注解
│ │ annotations_test.go
│ │
│ ├───controller
│ │ │ controller.go
│ │ │ event_handler.go // ResourceEventHandler
│ │ │ kong.go // Kong 相关函数
│ │ │
│ │ └───parser
│ │ parser.go // Store 转换为 Kong Store 函数
│ │
│ ├───election
│ │ election.go // 选举
│ │
│ ├───store
│ │ store.go // 封装 Store
│ │
│ ├───task
│ │ queue.go // 封装队列
│ │
│ └───utils // 工具类
│ k8s.go
│ reports.go // 匿名上报
│ types.go
│
└───pkg
├───apis
│ └───configuration // 序列化 JSON 结构定义
│
└───client
└───configuration // CRD Model 定义
2. 核心代码块
2.1 创建 Informer
- k8s 原生资源通过 client-go 包提供的 Informer 监听变化;
- CRD 资源通过封装在 pkg 目录下封装的 Informer 监听变化。
// k8s 原生资源 Informer
coreInformerFactory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(
kubeClient,
cliConfig.SyncPeriod, //时间间隔
informers.WithNamespace(cliConfig.WatchNamespace),
)
// CRD 自定义资源 Informer
kongInformerFactory := configinformer.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(
confClient,
cliConfig.SyncPeriod,
configinformer.WithNamespace(cliConfig.WatchNamespace),
)
...
// Informer 被添加回调函数处理 Event
ingInformer.AddEventHandler(reh)
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
for _, informer := range informers {
// 协程执行 Informer
go informer.Run(stopCh)
synced = append(synced, informer.HasSynced)
}
SyncPeriod 最小限制为 10 秒,默认监听所有 Namespace。
下面来看 Informer 返回的 Event 处理部分:
// 创建接收 Event 的通道
updateChannel := channels.NewRingChannel(1024)
// Informer 回调 Handler
reh := controller.ResourceEventHandler{
UpdateCh: updateChannel,
IsValidIngresClass: annotations.IngressClassValidatorFunc(cliConfig.IngressClass),
// 根据 ingress-class 注解过滤资源对象
}
...
// 主进程中接收通道信号,并压入队列定时处理
for {
select {
case event := <-n.updateCh.Out():
if v := atomic.LoadUint32(&n.isShuttingDown); v != 0 {
return
}
if evt, ok := event.(Event); ok {
glog.V(3).Infof("Event %v received - object %v", evt.Type, evt.Obj)
// 加入定时执行同步函数的队列
n.syncQueue.Enqueue(evt.Obj)
// TODO retry for ephermal error conditions
// This function is called outside the task queue because event
// information is currently shielded from the sync function.
// Sync function syncs everything, no matter what the event is
err := n.handleBasicAuthUpdates(evt)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("error handling basic-auth update: %v", err)
}
} else {
glog.Warningf("unexpected event type received: %T", event)
}
case <-n.stopCh:
return
}
}
2.2 创建资源锁竞争选举
Controller 可以部署分布式多实例,为了避免重复对 Admin API 进行操作,导致混乱,程序在启动阶段通过 k8s ConfigMap 资源锁进行选举 Leader。
选举有以下步骤:
- 创建 ConfigMapLock,基于 etcd 幂等性只有一个程序获得资源
- 抢到锁的实例定时 renew 续期
- 其他实例根据最后续期时间判断锁是否有效,否则竞争创建锁
// NewElector returns an instance of Elector based on config.
func NewElector(config Config) Elector {
pod, err := utils.GetPodDetails(config.Client)
if err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("unexpected error obtaining pod information: %v", err)
}
es := elector{
Config: config,
}
broadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
hostname, _ := os.Hostname()
recorder := broadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, apiv1.EventSource{
Component: "ingress-leader-elector",
Host: hostname,
})
// 定义 ConfigMapLock 资源锁结构
lock := resourcelock.ConfigMapLock{
ConfigMapMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Namespace: pod.Namespace,
Name: config.ElectionID},
Client: config.Client.CoreV1(),
LockConfig: resourcelock.ResourceLockConfig{
Identity: pod.Name,
EventRecorder: recorder,
},
}
ttl := 30 * time.Second
// 调用 client-go leaderelection 包进行选举
le, err := leaderelection.NewLeaderElector(
leaderelection.LeaderElectionConfig{
Lock: &lock,
LeaseDuration: ttl, // 锁有效时间
RenewDeadline: ttl / 2, // 续期间隔
RetryPeriod: ttl / 4,
Callbacks: config.Callbacks,
ReleaseOnCancel: true,
})
if err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("unexpected error starting leader election: %v", err)
}
// 储存选举信息
es.elector = le
return es
}
...
// 在执行同步函数开始时判断,非 Leader 直接退出
// If in-memory mode, each Kong instance runs with its own controller
if !n.cfg.Kong.InMemory &&
!n.elector.IsLeader() {
glog.V(2).Infof("skipping synchronization of configuration because I am not the leader.")
return nil
}
2.3 队列执行同步函数
2.3.1 创建队列
queue.go 文件里定义了队列结构体和运行函数,内部使用 client-go workqueue 包,队列配置有 RateLimit,避免频繁对 Admin API 进行操作。
来看一下 Queue 结构体定义。
type Queue struct {
// k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue 库
// queue is the work queue the worker polls
queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
// sync is called for each item in the queue
sync func(interface{}) error
// workerDone is closed when the worker exits
workerDone chan bool
// queue 元素 Key 生成函数
fn func(obj interface{}) (interface{}, error)
lastSync int64
}
// queue 中包含的结构体
// Element represents one item of the queue
type Element struct {
Key interface{}
Timestamp int64
}
fn() 使用 DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc 函数生成 API 资源的 Key,该函数会返回删除资源的 Key 或 namespace/name 格式的 Key。
关注队列消费的方法:
// worker processes work in the queue through sync.
func (t *Queue) worker() {
for {
key, quit := t.queue.Get()
if quit {
if !isClosed(t.workerDone) {
close(t.workerDone)
}
return
}
ts := time.Now().UnixNano()
// 判断队列内事件是否有效
item := key.(Element)
if t.lastSync > item.Timestamp {
glog.V(3).Infof("skipping %v sync (%v > %v)", item.Key, t.lastSync, item.Timestamp)
t.queue.Forget(key)
t.queue.Done(key)
continue
}
glog.V(3).Infof("syncing %v", item.Key)
// 对每个队列内元素执行 sync 函数
if err := t.sync(key); err != nil {
glog.Warningf("requeuing %v, err %v", item.Key, err)
// 执行错误,限速
t.queue.AddRateLimited(Element{
Key: item.Key,
Timestamp: time.Now().UnixNano(),
})
} else {
// 执行成功
t.queue.Forget(key)
t.lastSync = ts
}
t.queue.Done(key)
}
}
2.3.2 解析资源
parser.go 中 Build() 方法解析 k8s 内资源到自定义资源格式,主要职责为格式转换和将多个数据源的数据进行组合,生成期望的数据格式。
// Build creates a Kong configuration from Ingress and Custom resources
// defined in Kuberentes.
// It throws an error if there is an error returned from client-go.
func (p *Parser) Build() (*KongState, error) {
var state KongState
ings := p.store.ListIngresses()
tcpIngresses, err := p.store.ListTCPIngresses()
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("error listing TCPIngresses: %v", err)
}
// 解析、合并 Ingress、和自定义 TCPIngress 资源
// 生成 Service 和 Route
parsedInfo := p.parseIngressRules(ings, tcpIngresses)
// 关联 k8s Service 资源
// populate Kubernetes Service
for key, service := range parsedInfo.ServiceNameToServices {
// 通过 client-go Storer 获取 Service
k8sSvc, err := p.store.GetService(service.Namespace, service.Backend.Name)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("getting service: %v", err)
}
if k8sSvc != nil {
// 获取到 Service 则关联
service.K8sService = *k8sSvc
}
parsedInfo.ServiceNameToServices[key] = service
}
// add the routes and services to the state
for _, service := range parsedInfo.ServiceNameToServices {
state.Services = append(state.Services, service)
}
// 生成 Upstream 和 Target
state.Upstreams = p.getUpstreams(parsedInfo.ServiceNameToServices)
// 生成其他资源
// generate consumers and credentials
p.fillConsumersAndCredentials(&state)
// process annotation plugins
state.Plugins = p.fillPlugins(state)
// generate Certificates and SNIs
state.Certificates = p.getCerts(parsedInfo.SecretNameToSNIs)
// populate CA certificates in Kong
state.CACertificates, err = p.getCACerts()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &state, nil
}
2.3.2.1 资源结构定义
Controller 定义了一些结构体储存 k8s 资源和 Kong 对应的资源。
// KongState holds the configuration that should be applied to Kong.
type KongState struct {
Services []Service
Upstreams []Upstream
Certificates []Certificate
CACertificates []kong.CACertificate
Plugins []Plugin
Consumers []Consumer
}
// Service represents a service in Kong and holds routes associated with the
// service and other k8s metadata.
type Service struct {
kong.Service
Backend backend
Namespace string
Routes []Route
Plugins []kong.Plugin
K8sService corev1.Service
}
// Route represents a Kong Route and holds a reference to the Ingress
// rule.
type Route struct {
kong.Route
// Ingress object associated with this route
Ingress networking.Ingress
// TCPIngress object associated with this route
TCPIngress configurationv1beta1.TCPIngress
// Is this route coming from TCPIngress or networking.Ingress?
IsTCP bool
Plugins []kong.Plugin
}
...
结构体包含了 k8s 自身资源的信息,和解析到 Kong 资源格式的对应信息。
2.3.2.2 解析 Ingress
该方法的职能为排序去重 Ingress 规则,合并 TCPIngress 规则,创建
func (p *Parser) parseIngressRules(
// k8s Ingress 资源
ingressList []*networking.Ingress,
// 自定义 TCPIngress 资源
tcpIngressList []*configurationv1beta1.TCPIngress) *parsedIngressRules {
// 按照时间排序
sort.SliceStable(ingressList, func(i, j int) bool {
return ingressList[i].CreationTimestamp.Before(
&ingressList[j].CreationTimestamp)
})
sort.SliceStable(tcpIngressList, func(i, j int) bool {
return tcpIngressList[i].CreationTimestamp.Before(
&tcpIngressList[j].CreationTimestamp)
})
// generate the following:
// Services and Routes
var allDefaultBackends []networking.Ingress
secretNameToSNIs := make(map[string][]string)
serviceNameToServices := make(map[string]Service)
for i := 0; i < len(ingressList); i++ {
ingress := *ingressList[i]
ingressSpec := ingress.Spec
if ingressSpec.Backend != nil {
allDefaultBackends = append(allDefaultBackends, ingress)
}
processTLSSections(ingressSpec.TLS, ingress.Namespace, secretNameToSNIs)
for i, rule := range ingressSpec.Rules {
host := rule.Host
if rule.HTTP == nil {
continue
}
for j, rule := range rule.HTTP.Paths {
path := rule.Path
if strings.Contains(path, "//") {
glog.Errorf("ingress rule skipped in Ingress'%v/%v', "+
"'%v' is an invalid path", ingress.Namespace,
ingress.Name, path)
continue
}
if path == "" {
path = "/"
}
// 创建 Route 结构体
r := Route{
Ingress: ingress,
Route: kong.Route{
// TODO Figure out a way to name the routes
// This is not a stable scheme
// 1. If a user adds a route in the middle,
// due to a shift, all the following routes will
// be PATCHED
// 2. Is it guaranteed that the order is stable?
// Meaning, the routes will always appear in the same
// order?
Name: kong.String(ingress.Namespace + "." + ingress.Name + "." + strconv.Itoa(i) + strconv.Itoa(j)),
Paths: kong.StringSlice(path),
StripPath: kong.Bool(false),
PreserveHost: kong.Bool(true),
Protocols: kong.StringSlice("http", "https"),
RegexPriority: kong.Int(0),
},
}
if host != "" {
// Route 域名地址
r.Hosts = kong.StringSlice(host)
}
// 创建 Service 结构体
serviceName := ingress.Namespace + "." +
rule.Backend.ServiceName + "." +
rule.Backend.ServicePort.String()
service, ok := serviceNameToServices[serviceName]
if !ok {
service = Service{
// Kong 的 Service 对象
Service: kong.Service{
Name: kong.String(serviceName),
// Upstream 地址,后续创建 Upstream 使用相同地址
Host: kong.String(rule.Backend.ServiceName +
"." + ingress.Namespace + "." +
rule.Backend.ServicePort.String() + ".svc"),
Port: kong.Int(80),
Protocol: kong.String("http"),
Path: kong.String("/"),
ConnectTimeout: kong.Int(60000),
ReadTimeout: kong.Int(60000),
WriteTimeout: kong.Int(60000),
Retries: kong.Int(5),
},
Namespace: ingress.Namespace,
Backend: backend{
Name: rule.Backend.ServiceName,
Port: rule.Backend.ServicePort,
},
}
}
// 关联 Service 与 Route
service.Routes = append(service.Routes, r)
serviceNameToServices[serviceName] = service
}
}
}
return &parsedIngressRules{
SecretNameToSNIs: secretNameToSNIs,
ServiceNameToServices: serviceNameToServices,
}
}
2.3.2.3 解析 Endpoints
生成 Upstream 结构体:
func (p *Parser) getUpstreams(serviceMap map[string]Service) []Upstream {
var upstreams []Upstream
for _, service := range serviceMap {
// 这里的 Upstream 名称与 Service 里的 Host 地址一致
upstreamName := service.Backend.Name + "." + service.Namespace + "." + service.Backend.Port.String() + ".svc"
upstream := Upstream{
Upstream: kong.Upstream{
Name: kong.String(upstreamName),
},
Service: service,
}
// 获取 Targets
targets := p.getServiceEndpoints(service.K8sService,
service.Backend.Port.String())
upstream.Targets = targets
upstreams = append(upstreams, upstream)
}
return upstreams
}
获取 Endpoint 生成 Target 结构体:
// 接收 k8s Service 和 Ingress.Backend.ServicePort 参数
func (p *Parser) getServiceEndpoints(svc corev1.Service,
backendPort string) []Target {
var targets []Target
var endpoints []utils.Endpoint
var servicePort corev1.ServicePort
svcKey := svc.Namespace + "/" + svc.Name
for _, port := range svc.Spec.Ports {
// 查找 Ingress.Backend.ServicePort 和 Service.Port 对应的部分
// 获取 Port 资源对象
// targetPort could be a string, use the name or the port (int)
if strconv.Itoa(int(port.Port)) == backendPort ||
port.TargetPort.String() == backendPort ||
port.Name == backendPort {
servicePort = port
break
}
}
// Ingress with an ExternalName service and no port defined in the service.
if len(svc.Spec.Ports) == 0 &&
svc.Spec.Type == corev1.ServiceTypeExternalName {
// nolint: gosec
externalPort, err := strconv.Atoi(backendPort)
if err != nil {
glog.Warningf("only numeric ports are allowed in"+
" ExternalName services: %v is not valid as a TCP/UDP port",
backendPort)
return targets
}
servicePort = corev1.ServicePort{
Protocol: "TCP",
Port: int32(externalPort),
TargetPort: intstr.FromString(backendPort),
}
}
// 获取 Endpoint
endpoints = getEndpoints(&svc, &servicePort,
corev1.ProtocolTCP, p.store.GetEndpointsForService)
if len(endpoints) == 0 {
glog.Warningf("service %v does not have any active endpoints",
svcKey)
}
for _, endpoint := range endpoints {
target := Target{
Target: kong.Target{
Target: kong.String(endpoint.Address + ":" + endpoint.Port),
},
}
targets = append(targets, target)
}
return targets
}
p.store.GetEndpointsForService() 方法是 Storer 获取 Endpoint 的方法,Endpoints 结构体:
// +genclient
// +k8s:deepcopy-gen:interfaces=k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime.Object
// Endpoints is a collection of endpoints that implement the actual service. Example:
// Name: "mysvc",
// Subsets: [
// {
// Addresses: [{"ip": "10.10.1.1"}, {"ip": "10.10.2.2"}],
// Ports: [{"name": "a", "port": 8675}, {"name": "b", "port": 309}]
// },
// {
// Addresses: [{"ip": "10.10.3.3"}],
// Ports: [{"name": "a", "port": 93}, {"name": "b", "port": 76}]
// },
// ]
type Endpoints struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// Standard object's metadata.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// The set of all endpoints is the union of all subsets. Addresses are placed into
// subsets according to the IPs they share. A single address with multiple ports,
// some of which are ready and some of which are not (because they come from
// different containers) will result in the address being displayed in different
// subsets for the different ports. No address will appear in both Addresses and
// NotReadyAddresses in the same subset.
// Sets of addresses and ports that comprise a service.
// +optional
Subsets []EndpointSubset `json:"subsets,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=subsets"`
}
继续看获取 Endpoint 的方法:
// getEndpoints returns a list of <endpoint ip>:<port> for a given service/target port combination.
func getEndpoints(
s *corev1.Service,
port *corev1.ServicePort,
proto corev1.Protocol,
getEndpoints func(string, string) (*corev1.Endpoints, error),
) []utils.Endpoint {
upsServers := []utils.Endpoint{}
if s == nil || port == nil {
return upsServers
}
// avoid duplicated upstream servers when the service
// contains multiple port definitions sharing the same
// targetport.
adus := make(map[string]bool)
// 外部服务
// ExternalName services
if s.Spec.Type == corev1.ServiceTypeExternalName {
glog.V(3).Infof("Ingress using a service %v of type=ExternalName", s.Name)
targetPort := port.TargetPort.IntValue()
// check for invalid port value
if targetPort <= 0 {
glog.Errorf("ExternalName service with an invalid port: %v", targetPort)
return upsServers
}
return append(upsServers, utils.Endpoint{
Address: s.Spec.ExternalName,
Port: fmt.Sprintf("%v", targetPort),
})
}
// 解析 Service 的 ingress.kubernetes.io/service-upstream 注解
// 为 "true" 则交给 Kube-proxy 执行后续负载均衡操作
if annotations.HasServiceUpstreamAnnotation(s.Annotations) {
return append(upsServers, utils.Endpoint{
Address: s.Name + "." + s.Namespace + ".svc",
Port: fmt.Sprintf("%v", port.Port),
})
}
glog.V(3).Infof("getting endpoints for service %v/%v and port %v", s.Namespace, s.Name, port.String())
// 调用 client-go Storer 获取 Service 的 Endpoints
ep, err := getEndpoints(s.Namespace, s.Name)
if err != nil {
glog.Warningf("unexpected error obtaining service endpoints: %v", err)
return upsServers
}
for _, ss := range ep.Subsets {
for _, epPort := range ss.Ports {
// 不是 TCP 协议的 pass
if !reflect.DeepEqual(epPort.Protocol, proto) {
continue
}
var targetPort int32
if port.Name == "" {
// port.Name is optional if there is only one port
targetPort = epPort.Port
} else if port.Name == epPort.Name {
targetPort = epPort.Port
}
// check for invalid port value
if targetPort <= 0 {
continue
}
for _, epAddress := range ss.Addresses {
ep := fmt.Sprintf("%v:%v", epAddress.IP, targetPort)
// 如果有多个 Port 对应同一个 targetPort,
// 则跳过,不重复创建
if _, exists := adus[ep]; exists {
continue
}
ups := utils.Endpoint{
Address: epAddress.IP,
Port: fmt.Sprintf("%v", targetPort),
}
upsServers = append(upsServers, ups)
adus[ep] = true
}
}
}
glog.V(3).Infof("endpoints found: %v", upsServers)
return upsServers
}
2.3.3 同步资源
syncIngress() 方法中在解析完资源,生成 Kong 需要的数据结构后,调用 n.OnUpdate(state) 方法 Diff、Sync 到 Kong。
// 接收生成好的 Kong 数据库结构体,作为参数
// OnUpdate is called periodically by syncQueue to keep the configuration in sync.
// returning nil implies the synchronization finished correctly.
// Returning an error means requeue the update.
func (n *KongController) OnUpdate(state *parser.KongState) error {
// 调用 decK 库进行处理
targetContent := n.toDeckContent(state)
var customEntities []byte
var err error
var shaSum []byte
// disable optimization if reverse sync is enabled
if !n.cfg.EnableReverseSync {
// 生成 Hash 判断本次数据结构体和上次执行是否一致,
// 一致则不进行更新
shaSum, err = generateSHA(targetContent, customEntities)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if reflect.DeepEqual(n.runningConfigHash, shaSum) {
glog.Info("no configuration change, skipping sync to Kong")
return nil
}
}
// 调用 DB 更新函数
err = n.onUpdateDBMode(targetContent)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 记录本次操作的数据结构体 Hash
n.runningConfigHash = shaSum
glog.Info("successfully synced configuration to Kong")
return nil
}
这里引入了 Kong/decK 库处理 Kong 配置的同步,该库使用 Go 编写,提供了针对 Kong 配置的管理能力,能够导出 Kong 数据库配置到文件,也能从文件导入到 Kong,提供 Diff 和 Sync 等方法,内部使用多协程,算法优化提升执行速度。能够单独通过 CLI 使用,这里调用该库的 Diff 和 Sync 方法同步配置到 Kong。
n.toDeckContent(state) 方法将 KongState 结构转换为 decK 库使用的数据结构(一个文件序列化结构体)。
// Content represents a serialized Kong state.
type Content struct {
FormatVersion string `json:"_format_version,omitempty" yaml:"_format_version,omitempty"`
Info *Info `json:"_info,omitempty" yaml:"_info,omitempty"`
Workspace string `json:"_workspace,omitempty" yaml:"_workspace,omitempty"`
Services []FService `json:"services,omitempty" yaml:",omitempty"`
Routes []FRoute `json:"routes,omitempty" yaml:",omitempty"`
Consumers []FConsumer `json:"consumers,omitempty" yaml:",omitempty"`
Plugins []FPlugin `json:"plugins,omitempty" yaml:",omitempty"`
Upstreams []FUpstream `json:"upstreams,omitempty" yaml:",omitempty"`
Certificates []FCertificate `json:"certificates,omitempty" yaml:",omitempty"`
CACertificates []FCACertificate `json:"ca_certificates,omitempty" yaml:"ca_certificates,omitempty"`
PluginConfigs map[string]kong.Configuration `json:"_plugin_configs,omitempty" yaml:"_plugin_configs,omitempty"`
}
继续关注调用 Diff、Sync 的方法:
func (n *KongController) onUpdateDBMode(targetContent *file.Content) error {
client := n.cfg.Kong.Client
// 调用 Admin API 筛选 managed-by-conroller tag 下的
// 所有资源,到 State
// Get queries all the entities using client and returns
// all the entities in KongRawState.
rawState, err := dump.Get(client, dump.Config{
SelectorTags: n.getIngressControllerTags(),
})
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "loading configuration from kong")
}
// Get builds a KongState from a raw representation of Kong.
currentState, err := state.Get(rawState)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Get process the fileContent and renders a RawState.
// IDs of entities are matches based on currentState.
rawState, err = file.Get(targetContent, file.RenderConfig{
CurrentState: currentState,
KongVersion: n.cfg.Kong.Version,
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Get builds a KongState from a raw representation of Kong.
targetState, err := state.Get(rawState)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Diff, Sync
syncer, err := diff.NewSyncer(currentState, targetState)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "creating a new syncer")
}
syncer.SilenceWarnings = true
//client.SetDebugMode(true)
_, errs := solver.Solve(nil, syncer, client, n.cfg.Kong.Concurrency, false)
if errs != nil {
return deckutils.ErrArray{Errors: errs}
}
return nil
}
dump.Get() 方法调用 Admin API 获取 managed-by-controller tag 下所有的资源,加载到内存。
该方法调用 decK 生成了 k8s 环境下的资源状态,和通过 Admin API 查询到的 Kong DB 里的资源状态,接下来会调用 decK 库进行 diff 和 sync,将创建 Kong DB 里没有的资源,删除 k8s 环境下没有的资源,同步更新 Kong 的资源。
2.5 ingress-nginx 分析
ingress-nginx 是 Kubernetes 的官方 Ingress Controller 项目,其 Controller 部署的启动逻辑与上文所述 Kong 的 Ingress Controller 基本一致,甚至后者部分代码是直接从 ingress-nginx Copy 过来的,代码里还残留着 NGINX 字样。
2.5.1 SSL Proxy 分析
ingress-nginx 提供了 SSL Passthrough 功能,使得加密流量直接通过 443 端口传到后端服务器,这里引用一篇文章清晰明了的解释。
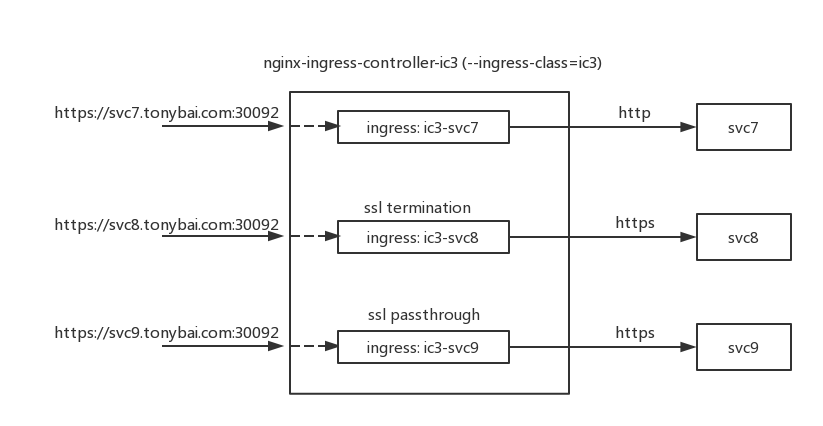
svc7: 是对传统通信模型的“复现”,即 Client 与 Nginx 间采用 HTTPS 加密通信,但 Nginx 与 svc7 间则是明文的 HTTP 通信;
svc8: 是 ssl-termination 的安全配置模型,即 Client 与 svc8 的 HTTPS 通信分为“两段”,Client 与 Nginx 建立 HTTPS 连接后,Nginx 将 Client 提交的加密请求解密后,再向 svc8 发起 HTTPS 请求,并重新加密请求数据。这种 Client 端 SSL 的过程在反向代理或负载均衡器终结的 HTTPS 通信方式被称为“ssl-termination”。
svc9: 是 ssl-passthrough 的安全配置模型,即 Nginx 不会对 Client 的 HTTPS Request 进行解密,而是直接转发给 backend 的 svc9 服务,Client 端的 SSL 过程不会终结于 Nginx,而是在 svc9 对应的 Pod 中终结。这种 HTTPS 通信方式被称为”ssl-passthrough”。这种配置模型尤其适合 backend service 对 Client 端进行 client certificate 验证的情况,同时也降低了 Nginx 加解密的性能负担。
Ingress Controller 启动时如果有 --enable-ssl-passthrough 参数则内部 Go 程序占用 443 端口提供代理功能。
// Controller 中判断是否启用 ssl 透传
if n.cfg.EnableSSLPassthrough {
n.setupSSLProxy()
}
func (n *NGINXController) setupSSLProxy() {
cfg := n.store.GetBackendConfiguration()
sslPort := n.cfg.ListenPorts.HTTPS
proxyPort := n.cfg.ListenPorts.SSLProxy
klog.InfoS("Starting TLS proxy for SSL Passthrough")
n.Proxy = &TCPProxy{
Default: &TCPServer{
Hostname: "localhost",
IP: "127.0.0.1",
Port: proxyPort,
ProxyProtocol: true,
},
}
// sslPort 为 443 端口
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%v", sslPort))
if err != nil {
klog.Fatalf("%v", err)
}
// accept TCP connections on the configured HTTPS port
go func() {
for {
var conn net.Conn
var err error
conn, err = listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Error accepting TCP connection: %v", err)
continue
}
klog.V(3).InfoS("Handling TCP connection", "remote", conn.RemoteAddr(), "local", conn.LocalAddr())
go n.Proxy.Handle(conn)
}
}()
}
Nginx 在被 Go 程序占用 443 端口后,会在 proxyPort 端口(默认 442)上监听 HTTPS 请求。
生成 http 块下 server listen 的部分是这样的:
func httpsListener(addresses []string, co string, tc config.TemplateConfig) []string {
out := make([]string, 0)
for _, address := range addresses {
lo := []string{"listen"}
if tc.IsSSLPassthroughEnabled {
if address == "" {
lo = append(lo, fmt.Sprintf("%v", tc.ListenPorts.SSLProxy))
} else {
lo = append(lo, fmt.Sprintf("%v:%v", address, tc.ListenPorts.SSLProxy))
}
if !strings.Contains(co, "proxy_protocol") {
lo = append(lo, "proxy_protocol")
}
} else {
if address == "" {
lo = append(lo, fmt.Sprintf("%v", tc.ListenPorts.HTTPS))
} else {
lo = append(lo, fmt.Sprintf("%v:%v", address, tc.ListenPorts.HTTPS))
}
}
lo = append(lo, co)
lo = append(lo, "ssl")
if tc.Cfg.UseHTTP2 {
lo = append(lo, "http2")
}
lo = append(lo, ";")
out = append(out, strings.Join(lo, " "))
}
return out
}
通过传参渲染 Go 模板,最终生成的 http 块中其中一个 server 的示例。
启用 ssl passthrough 功能后,所有 443 流量经过 Go 程序处理,Nginx 上只监听 442 端口。
http {
## start server svc.test.com
server {
server_name svc.test.com;
listen 80;
listen 442 proxy_protocol ssl http2;
location / {
proxy_pass http://default-svc;
}
}
## end server
}
内部的请求分发在 balancer_by_lua_block 块中调用 Lua 脚本处理,这里不做详细描述。
Go 程序通过读取请求前 4k 字节,解析出 SNI 域名,查找后端服务器。
/* This function is basically all most folks want to invoke out of this
* jumble of bits. This will take an incoming TLS Client Hello (including
* all the fuzzy bits at the beginning of it - fresh out of the socket) and
* go ahead and give us the SNI Name they want. */
func GetHostname(data []byte) (string, error) {
if len(data) == 0 || data[0] != 0x16 {
return "", fmt.Errorf("Doesn't look like a TLS Client Hello")
}
extensions, err := GetExtensionBlock(data)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
sn, err := GetSNBlock(extensions)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
sni, err := GetSNIBlock(sn)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return string(sni), nil
}
如果没有找到对应的后端服务器(没有开启 SSL 透传功能),则传递到默认的 Nginx 442 端口,交给 Nginx 去处理 HTTPS 请求。
// Get returns the TCPServer to use for a given host.
func (p *TCPProxy) Get(host string) *TCPServer {
if p.ServerList == nil {
return p.Default
}
for _, s := range p.ServerList {
if s.Hostname == host {
return s
}
}
return p.Default
}
处理数据流:
// Handle reads enough information from the connection to extract the hostname
// and open a connection to the passthrough server.
func (p *TCPProxy) Handle(conn net.Conn) {
defer conn.Close()
data := make([]byte, 4096)
length, err := conn.Read(data)
if err != nil {
klog.V(4).ErrorS(err, "Error reading the first 4k of the connection")
return
}
proxy := p.Default
hostname, err := parser.GetHostname(data[:])
if err == nil {
klog.V(4).InfoS("TLS Client Hello", "host", hostname)
proxy = p.Get(hostname)
}
if proxy == nil {
klog.V(4).InfoS("There is no configured proxy for SSL connections.")
return
}
hostPort := net.JoinHostPort(proxy.IP, fmt.Sprintf("%v", proxy.Port))
clientConn, err := net.Dial("tcp", hostPort)
if err != nil {
return
}
defer clientConn.Close()
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Error writing Proxy Protocol header")
clientConn.Close()
} else {
_, err = clientConn.Write(data[:length])
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Error writing the first 4k of proxy data: %v", err)
clientConn.Close()
}
}
pipe(clientConn, conn)
}
func pipe(client, server net.Conn) {
doCopy := func(s, c net.Conn, cancel chan<- bool) {
io.Copy(s, c)
cancel <- true
}
cancel := make(chan bool, 2)
go doCopy(server, client, cancel)
go doCopy(client, server, cancel)
select {
case <-cancel:
return
}
}
官方文档中描述该功能会造成不可忽略的性能影响。